



Next: 6. Stochastic Optimization
Up: csahtml
Previous: 5.5 Miscellaneous Topics on
-
- 1
-
Alon, U., Barkai, N., Notterman, D.A. et al. (1999).
Broad patterns of gene expression revealed by clustering analysis of
tumor and normal colon tissues probed by oligonucleotide arrays.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 96:6745-6750.
- 2
-
Bailey, T.L. and Elkan, C. (1995). Unsupervised learning of
multiple motifs in biopolymers using expectation maximization.
Machine Learning, 21:51-80.
- 3
-
Baker, S.G. (1992). A simple method for computing the
observed information matrix when using the EM algorithm with
categorical data. Journal of Computational and Graphical
Statistics, 1:63-76.
- 4
-
Basford, K.E., Greenway, D.R., McLachlan, G.J., and
Peel, D. (1997). Standard errors of fitted means under normal mixture
models. Computational Statistics, 12:1-17.
- 5
-
Baum, L.E., Petrie, T., Soules, G., and Weiss, N. (1970).
A maximisation technique occurring in the statistical analysis of
probabilistic functions of Markov processes. Annals of
Mathematical Statistics, 41:164-171.
- 6
-
Besag, J. (1986). On the statistical analysis of dirty
pictures. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
48:259-302.
- 7
-
Booth, J.G. and Hobert, J.P. (1999). Maximizing generalized
linear mixed model likelihoods with an automated Monte Carlo EM
algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
61:265-285.
- 8
-
Bradley, P.S., Fayyad, U.M., and Reina, C.A. (1998). Scaling EM
(expectation-maximization) clustering to large databases. Technical
Report No. MSR-TR-98-35 (revised February, 1999), Microsoft Research,
Seattle.
- 9
-
Breslow, N.E. and Clayton, D.G. (1993). Approximate inference
in generalized linear mixed models. Journal of the American
Statistical Association, 88:9-25.
- 10
-
Casella, G. and George, E.I. (1992). Explaining the Gibbs
sampler. American Statistician, 46:167-174.
- 11
-
Cramér, H. (1946). Mathematical Methods of
Statistics. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.
- 12
-
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., and Rubin, D.B. (1977).
Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
39:1-38.
- 13
-
Efron, B. (1979). Bootstrap methods: another look at the
jackknife. Annals of Statistics, 7:1-26.
- 14
-
Efron, B. and Tibshirani, R. (1993). An Introduction to the
Bootstrap. Chapman & Hall, London.
- 15
-
Fessler, J.A. and Hero, A.O. (1994). Space-alternating
generalized expectation-maximization algorithm.
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,
42:2664-2677.
- 16
-
Flury, B. and Zoppé, A. (2000). Exercises in EM.
American Statistician, 54:207-209.
- 17
-
Gelfand, A.E. and Smith, A.F.M. (1990). Sampling-based
approaches to calculating marginal densities.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
85:398-409.
- 18
-
Geman, S. and Geman, D. (1984). Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs
distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
6:721-741.
- 19
-
Hastings, W.K. (1970). Monte Carlo sampling methods using
Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika, 57:97-109.
- 20
-
Jamshidian, M. and Jennrich, R.I. (2000). Standard errors
for EM estimation.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
62:257-270.
- 21
-
Lawley, D.N. and Maxwell, A.E. (1971). Factor Analysis as
a Statistical Method. Butterworths, London, second edition.
- 22
-
Little, R.J.A. and Rubin, D.B. (2002). Statistical Analysis
with Missing Data. Wiley, New York, second edition.
- 23
-
Liu, C. and Rubin, D.B. (1994). The ECME algorithm: a simple
extension of EM and ECM with faster monotone convergence.
Biometrika, 81:633-648.
- 24
-
Liu, C. and Rubin, D.B. (1998). Maximum likelihood estimation
of factor analysis using the ECME algorithm with complete and
incomplete data. Statistica Sinica, 8:729-747.
- 25
-
Liu, C., Rubin, D.B., and Wu, Y.N. (1998). Parameter
expansion to accelerate EM: the PX-EM algorithm. Biometrika,
85:755-770.
- 26
-
Louis, T.A. (1982). Finding the observed information
matrix when using the EM algorithm.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
44:226-233.
- 27
-
Lystig, T.C. and Hughes, J.P. (2002). Exact computation of
the observed information matrix for hidden Markov models.
Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics,
11:678-689.
- 28
-
McCullagh, P.A. and Nelder, J. (1989). Generalized Linear
Models. Chapman & Hall, London, second edition.
- 29
-
McCulloch, C.E. (1997). Maximum likelihood algorithms for
generalized linear mixed models.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
92:162-170.
- 30
-
McLachlan, G.J. (1992). Discriminant Analysis and
Statistical Pattern Recognition. Wiley, New York.
- 31
-
McLachlan, G.J. and Basford, K.E. (1988). Mixture
Models: Inference and Applications to Clustering. Marcel Dekker,
New York.
- 32
-
McLachlan, G.J., Bean, R.W., and Peel, D. (2002). A mixture
model-based approach to the clustering of microarray expression
data. Bioinformatics, 18:413-422.
- 33
-
McLachlan, G.J. and Krishnan, T. (1997). The EM Algorithm
and Extensions. Wiley, New York.
- 34
-
McLachlan, G.J. and Peel, D. (2000). Finite Mixture Models.
Wiley, New York.
- 35
-
McLachlan, G.J., Peel, D., and Bean, R.W. (2003). Modelling
high-dimensional data by mixtures of factor analyzers.
Computational Statistics & Data Analysis,
41:379-388.
- 36
-
Meilijson, I. (1989). A fast improvement of the EM
algorithm in its own terms.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
51:127-138.
- 37
-
Meng, X.L. (1994). On the rate of convergence of the
ECM algorithm. Annals of Statistics, 22:326-339.
- 38
-
Meng, X.L. and Rubin, D.B. (1991). Using EM to obtain asymptotic
variance-covariance matrices: the SEM algorithm.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
86:899-909.
- 39
-
Meng, X.L. and Rubin, D.B. (1993). Maximum likelihood
estimation via the ECM algorithm: a general framework. Biometrika,
80:267-278.
- 40
-
Meng, X.L. and van Dyk, D. (1997). The EM algorithm - an
old folk song sung to a fast new tune.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
59:511-567.
- 41
-
Moore, A.W. (1999). Very fast EM-based mixture model
clustering using multiresolution
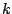 d-trees. In Kearns, M.S., Solla,
S.A., and Cohn, D.A., editors, Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 11, pages 543-549. MIT Press, MA.
d-trees. In Kearns, M.S., Solla,
S.A., and Cohn, D.A., editors, Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 11, pages 543-549. MIT Press, MA.
- 42
-
Neal, R.M. and Hinton, G.E. (1998). A view of the EM algorithm that
justifies incremental, sparse, and other variants. In Jordan, M.I.,
editor, Learning in Graphical Models, pages 355-368. Kluwer,
Dordrecht.
- 43
-
Nettleton, D. (1999). Convergence properties of the EM
algorithm in constrained parameter spaces.
Canadian Journal of Statistics, 27:639-648.
- 44
-
Newton, M.A. and Raftery, A.E. (1994). Approximate Bayesian
inference with the weighted likelihood bootstrap.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
56:3-48.
- 45
-
Ng, S.K. and McLachlan, G.J. (2003a). On the choice of the
number of blocks with the incremental EM algorithm for the fitting
of normal mixtures. Statistics and Computing,
13:45-55.
- 46
-
Ng, S.K. and McLachlan, G.J. (2003b). On some variants of
the EM algorithm for the fitting of finite mixture models.
Austrian Journal of Statistics, 32:143-161.
- 47
-
Qian, W. and Titterington, D.M. (1992). Stochastic relaxations
and EM algorithms for Markov random fields.
Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 40:55-69.
- 48
-
Richardson, S. and Green, P.J. (1997). On Bayesian analysis of
mixtures with an unknown number of components.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
59:731-792 (correction (1998),
pp. 661).
- 49
-
Robert, C.P., Celeux, G., and Diebolt, J. (1993). Bayesian
estimation of hidden Markov chains: A stochastic implementation.
Statistics & Probability Letters, 16:77-83.
- 50
-
Roberts, G.O. and Polson, N.G. (1994). On the geometric
convergence of the Gibbs sampler.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
56:377-384.
- 51
-
Sahu, S.K. and Roberts, G.O. (1999). On convergence of the
EM algorithm and the Gibbs sampler.
Statistics and Computing, 9:55-64.
- 52
-
Sexton, J. and Swensen, A.R. (2000). ECM algorithms that
converge at the rate of EM. Biometrika,
87:651-662.
- 53
-
Ueda, N. and Nakano, R. (1998). Deterministic annealing EM
algorithm. Neural Networks, 11:271-282.
- 54
-
van Dyk, D.A. and Meng, X.L. (2001). The art of data
augmentation. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics,
10:1-111.
- 55
-
van Dyk, D.A. and Tang, R. (2003). The one-step-late PXEM
algorithm. Statistics and Computing, 13:137-152.
- 56
-
van't Veer, L.J., Dai, H., van de Vijver, M.J. et al. (2002). Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of
breast cancer. Nature, 415:530-536.
- 57
-
Wei, G.C.G. and Tanner, M.A. (1990). A Monte Carlo
implementation of the EM algorithm and the poor man's data
augmentation algorithms.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
85:699-704.
- 58
-
Wright, K. and Kennedy, W.J. (2000). An interval analysis
approach to the EM algorithm.
Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics,
9:303-318.
- 59
-
Wu, C.F.J. (1983). On the convergence properties of the
EM algorithm. Annals of Statistics, 11:95-103.
Subsections