

Up: csahtml
Previous: References
- 3D Visual Data Mining (3DVDM) System
- 10.5.2
- abbreviation method
- 12.3.8
- acceptance rate
- 3.3
- empirical
- 11.4.1
- acceptance-complement method
- 2.8.2
- access specifier
- 13.2.5
- accumulated proportion
- 6.2.1.1
- adaptive mixtures
- 5.4
- adaptive SPSA
- 6.3.3
- adaptivity
- 11.5.1
| 11.5.1
| 11.5.2
- invalid
- 11.5.1
- add-with-carry
- 2.3.6
- additive models
- 5.5
| 10.2.3
- address spoofing
- 5.3
- adjusted dependent variable
- 7.3.3
- aesthetics
- 11.8
- affine equivariance
- 9.3.1
| 9.3.5
- affine transformation
- 9.2.1
- AICc
- 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
- aircraft design
- 6.3.3
- Akaike's information criterion (AIC)
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 7.3.5
| 8.1.3.1
| 11.2.3
| 15.2.2.1
- algebra
- 11.3
- algebraic curve fitting
- 6.3.2
- algebraic surface fitting
- 6.3.2
- alias method
- 2.8.2
- allowable splits
- 14.3.1
- alterning expectation-conditional maximization (AECM) algorithm
- 5.4.3.1
| 5.5.3.1
- Amdahl's law
- 8.2.2.1
- anaglyphs
- 10.5
| 10.5.1
- Analysis of Functional Neuroimages (AFNI)
- 4.5.1
- analysis of variance
- 9.5
- Andrews plot
- 10.3.9
- annealed entropy
- 15.2.3
- anomaly detection
- 5.1
- antithetic variables
- 2.3.2.2
- antithetic variates
- 3.2
- aperiodic
- 3.2.1
- applications
- 15.7
- approximate distance
- 6.3.2.2
- approximations
- 12.3.3
- AR model
- 11.2.1
| 11.2.3
| 11.4.3
- order
- 11.2.1
- ArcView/XGobi
- 10.5.2
- ArcView/XGobi/XploRe
- 10.6.1
- arithmetic mean
- 9.1.3
- artificial intelligence
- 6.4.1
- asset returns
- 2.1
| 2.3
- association rules
- 13.4.4
- asymptotic bias
- 5.3.1
- asymptotic distribution
- 6.3.3
- asymptotic normality
- 9.3.2
- asymptotic relative efficiency
- 9.1.1
| 12.1.2
- asymptotic variance
- 5.3.2
| 9.1.2
- asymptotically random
- 2.4.2
- attack propagation
- 5.7
- autocorrelation plots
- 3.3.2.1
- autocorrelation time
- 3.2.2
- automatic methods
- 2.8.1
| 2.8.8
- auxiliary variables
- 3.5
- averaged shifted histogram (ASH)
- 10.3.10
| 10.4.3
| 4.3.3
- backscatter
- 5.3
| 5.5
| 5.5
- bandwidth
- Choosing
| 5.2.1
| 5.2.2
| 5.3
- bar chart
- 10.3.11
- base class
- 13.4
- base-line intensity
- 12.4
- batch means
- 3.2.2
- Bayes
- optimal
- 15.2.1
- theorem
- 11.2.3
- Bayes factor
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.5
| 1.5
| 1.5
| 1.5
| 1.5
| 11.2.2
| 2.4.1
- approximation
- 11.3.3
| 11.3.3
- computation
- 11.2.3
- Bayesian
- hierarchical structures
- 11.4.2
- software
- 11.6
- Bayesian classifiers
- 13.4.3
- Bayesian framework
- 5.1.1
- Gibbs sampler
- 5.5.1
| 5.5.2
| 5.5.2
| 5.5.3.2
- MAP estimate
- 5.5.1
| 5.5.2
- MCMC
- 5.5.1
| 5.5.2
- Bayesian inference
- 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.4
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.2
- Bayesian information criterion (BIC)
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.5
| 7.3.5
- Bayesian statistics
- 3.1
| 11.1
- Beowulf class cluster
- 8.2.1.2
- Bernoulli data
- 7.1
- Bertillon, Alphonse
- 11.4.2
- BFGS algorithm
- 2.3.3
- bias
- 5.3.1
| 9.1.2
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.6
| 9.3.3
| 9.3.4
- function
- 9.3.4
- functional
- 9.3.3
- bias estimation
- 5.4.1.3
- bias-variance tradeoff
- 1.1
| 1.2
| 1.2
| 1.2
| 1.2.1
| 5.3
- binary data
- 7.1
- binary representation
- 6.4.2
- binary response data
- 3.3.2
- Binary Response Model
- 10.4
- binary search
- 2.8.1
- binary tree
- 14.1
- binomial distribution
- 7.2.1
| 11.2.2
- bioinformatics
- 5.5.3.1
- bioprocess control
- 6.3.3
- birth-and-death process
- 11.4.3
- birthday spacings test
- 2.6
- bisquare function
- 5.2.1
- bivariate histogram
- 4.2.1
- blind random search
- 6.2.2
| 6.2.2.1
- block bootstrap
- 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.7
- block design
- 4.3.1
- blocks
- 3.1
- blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) contrast
- 4.2.3.3
- Bonferonni correction
- 4.4.2.2
- boosting
- 15.4.1
- bootstrap
- 5.3.5
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 3.2
| 5.4.3
| 14.7
- nonparametric
- 5.3.5
- smooth
- 11.5.2
- bootstrap for dependent data
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.4
| 2.4.7
- Boston Housing data
- 12.3.5
| 12.3.5
| 12.3.8
| 12.3.8
| 12.3.8
| 12.3.8
- boundary bias
- 5.2.1
- bounded algebraic curve
- 6.3.2.5
- boxplot
- 9.1.1
- brain activation
- 4.3.1
- Brain Voyager
- 4.5.1
- breakdown
- 9.1.2
| 9.2.3
| 9.3.3
- breakdown point
- 9.1.2
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.6
| 9.3.2
| 9.4.3
| 9.4.4
- breakdown point of M-functional
- 9.3.3
- Breslow-Peto method
- 12.3.1
| 12.3.1
| 12.3.2
- bridge estimator
- 11.3.3
- bridge sampling
- 11.3.3
| 11.3.3
| 11.3.3
- brush-tour
- 10.3.5
- brushing
- 10.3.2
| 12.3.5
- brushing with hue and saturation
- 10.3.10
- burn-in
- 3.3
- candidate generating density
- 3.3
- canonical link
- 7.2.2
| 7.3.4
- cascade algorithm
- 7.4.1
- Castillo-Hadi model
- 12.2
- categorization
- 7.4
- Cauchy distribution
- 9.2.3
- CAVE Audio Visual Experience Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE)
- 10.5.2
- censored data
- 5.5.3
| 14.5
- central limit theorem
- 9.1.3
| 11.3.1
- characteristic polynomial
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
- chi-squared-test
- 7.3.5
- choice
- brand
- 2.2
| 2.2.1.3
- discrete
- 2.1
| 2.2
- probabilities
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.2.2
- transport mode
- 2.2
- Cholesky decomposition
- 4.1.1
- chromosome
- 6.4.1
| 6.4.2
- class
- 13.2.3
- class diagram
- 13.3
- class hierarchy
- 13.4.1
- class interface
- 13.2.5
- classification
- 14.1
| 15.1
- clustered data
- 7.5.7
- clustering
- 13.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2.2
- duration
- 2.3.5
- volatility
- 2.3
- coefficient of determination
- 8.1.3.1
- coefficient of variation
- 12.1.2
| 12.1.2
- collision test
- 2.6
| 2.6
- color
- 12.3.7
- color model
- 10.3.8
| 10.5.1
- combined generators
- 2.3.4
| 2.4.6
- command streams
- 5.6
- common cumulative mean function
- 12.4
- common parameter
- 12.4.3
- common random numbers
- 3.2
- common trend parameter
- 12.4
- complete-data
- information matrix
- 5.3.5
- likelihood
- 5.1.2
| 5.2.1
- log likelihood
- 5.2.1
| 5.2.3
| 5.3.1
| 5.3.2
| 5.3.3
| 5.3.3
| 5.4.1.1
| 5.4.2.2
- problem
- 5.1.2
| 5.3.1
| 5.3.3
- sufficient statistics
- 5.4.2.2
- completion
- 11.4.2
- complexity
- 15.2.3
- complexity parameter
- 14.2.2
- composition method
- 2.8.7
- COMPSTAT Conferences
- 1.2.2
- computational effort
- 11.3.1
- computational inference
- 1.1
| 1.3.1
| 1.3.2
| 1.3.2
- computational statistics
- 1.1
- conditional likelihood
- 12.3.3
| 12.4.2
| 12.4.4
- conditional tests
- 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
- Conditional VaR
- 1.1
- conditioned choropleth maps (CCmaps)
- 10.6.3
- confidence
- 13.5.1.4
- confidence interval
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 5.4.2.1
| 9.1.2
| 9.2.5
| 9.3.2
- confidence level
- 11.2.2
- confidence regions
- 11.2.2
- conjugate gradient method
- 4.3.5.3
- consistency
- 15.2.2
| 15.2.2
| 15.2.2.2
- uniform convergence
- 15.2.2.2
- consistent
- 9.1.3
- constraints
- 6.1.4
| 6.4.4
- constructor
- 13.2.3.1
- contingency table
- 7.5.5
- continuum regression
- 8.1.7
- ridge regression
- 8.1.7
- contour shell
- 10.3.10
- contour surface
- 10.3.10
- control variables
- 2.3.2.2
- convergence
- 5.2.1
| 5.2.3
| 5.2.3
| 5.2.5
| 5.4.2.1
| 5.4.2.1
| 5.4.2.2
| 5.4.3.1
- monotonicity property
- 5.2.3
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.2.1
| 5.4.3.1
- speeding up
- 5.4.3
| 5.4.3.2
| 5.4.3.2
| 5.4.3.2
- convergence assessment
- 11.3.1
- convergence theory
- 6.2.2.2
| 6.3.2
- convolution method
- 2.8.7
- coordinates
- 11.7
- copula
- Archimedean
- 1.4
- elliptical
- 1.4
- estimation
- 1.4
- simulation
- conditional distributions method
- 1.4
- cost-complexity
- 14.2.2
- count data
- 3.8.2
| 7.1
- count model
- 2.4.2.2
- counting process
- 12.4
| 12.4.2
- covariance functional
- 9.3.4
- covariate
- 9.4.1
| 12.3
- covering numbers
- 15.2.3
- Cox model
- 12.3
| 12.3.2
- Cox's discrete model
- 12.3.3
- critical sampling
- Resolution
- cross
- 11.3.1.1
| 11.3.3.1
| 11.10.1.1
- cross validation
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 5.4.1.1
| 8.1.3.4
| 14.2.2
- crossover
- 6.4.2
| 6.4.2
- CrystalVision
- 10.4
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.5.2
- cumulative logit model
- 7.5.4
- cumulative mean function
- 12.4.2
- curse of dimension
- Rates
| 5.5
| 11.3.2
| 11.4.1
- cyclic menu
- 12.3.3
- data augmentation
- 3.5
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.2
- data mining (DM)
- 5.4.3.2
| 10.1
- Data Viewer
- 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
- data visualization
- 4.2.1
- DataDesk
- Web
- dataflow
- 11.1.1
- daughter node
- 14.2.1
- DC shifts
- 4.3.3.1
- Decision theory
- 11.2.1
- decision trees
- 13.4.3
| 13.5.1.1
| 14.1
- decomposition algorithm
- 7.4.1
- defensive sampling
- 11.5.2
- degrees of freedom
- 1.2
| 1.3
| 5.3.3
- denial of service attack
- 5.1
| 5.3
| 5.5
| 5.5
| 5.5
- density estimation
- 5.5.3
| 5.5.3.2
- dependent data
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
- descriptive modeling
- 13.4.2
- design matrix
- 5.2.2
- design of experiments
- 3.1
- destructor
- 13.2.3.1
- deterministic annealing EM (DAEM) algorithm
- 5.3.4
- deterministic simulation
- 3.1
| 3.5.1
- Deutsche Aktienindex (DAX)
- 1.2.5
| 1.3.3
- deviance
- 7.3.2
- penalized
- 11.2.3
- deviance information criterion (DIC)
- 11.2.3
- Diamond Fast
- 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
- differentiable
- 9.1.3
| 9.2.5
- digamma function
- 12.1.2
- dimension
- high
- 11.2.1
| 11.5.1
- matching
- 11.4.3
- unbounded
- 11.2.1
| 11.2.3
- unknown
- 11.4.3
- dimension reduction
- 5.4.2.2
| 5.4.2.2
| 5.5
- Dimension reduction methods of explanatory variables
- 6.4
- Dirichlet distribution
- 2.4.2.2
- discrepancy
- 2.2.3
- discrete logistic model
- 12.3
- discrete optimization
- 6.1.2
| 6.3.3
- dispersion parameter
- 7.3.4
- distributed memory
- 8.2.1
- distribution
 -stable
-stable
- 1.2
 -stable
-stable
- 1.2
 -stable
-stable
- characteristic function
- 1.2.1
 -stable
-stable
 parametrization
parametrization
- 1.2.1
 -stable
-stable
 parametrization
parametrization
- 1.2.1
 -stable
-stable
- density function
- 1.2.2
 -stable
-stable
- distribution function
- 1.2.2
 -stable
-stable
- direct integration method
- 1.2.2
 -stable
-stable
- STABLE program
- 1.2.2
 -stable
-stable
- simulation
- 1.2.3
 -stable
-stable
- Fama-Roll method
- 1.2.4.1
 -stable
-stable
- method of moments
- 1.2.4.2
 -stable
-stable
- regression method
- 1.2.4.2
 -stable
-stable
- regression method
- 1.2.4.2
 -stable
-stable
- maximum likelihood estimation
- 1.2.4.3
 -stable
-stable
- STABLE program
- 1.2.4.3
- binomial
- 7.2
| 11.2.2
- Cauchy
- 1.2.1
- folded
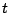
- 11.3.2
- Gaussian
- 1.2.1
- generalized hyperbolic
- density function
- 1.3
- maximum likelihood estimation
- 1.3.2.1
| 1.3.2.1
- mean
- 1.3
- simulation
- 1.3.1
- variance
- 1.3
- generalized inverse Gaussian (GIG)
- 1.3
- simulation
- 1.3.1
| 1.3.1
| 1.3.1
- hyperbolic
- 1.3
| 1.3
- density function
- 1.3
| 1.3
- inverse
- 1.3.3
- inverse Gaussian (IG)
- simulation
- 1.3.1
- Lévy
- 1.2.1
- Lévy stable
- 1.2
- mixture
- 11.4.2
| 11.4.3
- normal inverse Gaussian (NIG)
- density function
- 1.3
- simulation
- 1.3.1
- tail estimates
- 1.3.2.1
- tails
- 1.3
- predictive
- 11.2.1
- proposal
- 11.3.2
- stable Paretian
- 1.2
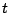
- 11.3.2
- target
- 11.4
- truncated stable (TLD)
- 1.2.6
- characteristic function
- 1.2.6
- dot plot
- 4.2.1
- doubledecker plot
- 13.5.2.3.1
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.2.5
| 1.3.3
- downweighting outlying observations
- 9.2.3
- dual lattice
- 2.3.2
| 2.4.3
- dynamic duration model/analysis
- 2.1
| 2.3
| 2.3.5
- E-step (Expectation step)
- 5.1.2
| 5.2.1
| 6.3.3.1
- exponential family
- 5.2.1
- factor analysis model
- 5.4.2.2
- failure-time data
- 5.3.2
- generalized linear mixed models (GLMM)
- 5.4.1.1
- Monte Carlo
- 5.4.1
| 5.4.1.1
- nonapplicability
- 5.3.3
- normal mixtures
- 5.3.1
- early binding
- 13.5.1
- effective number of parameters
- 5.3.3
- efficiency
- 9.2.3
| 9.2.6
- efficiency of the sample mean
- 12.1.2
- eigenvalues
- 4.4
- inverse iterations
- 4.4.6
- Jacobi method
- 4.4.2
- LR method
- 4.4.5
- power method
- 4.4.1
- QR method
- 4.4.4
- eigenvectors
- 4.4
- electroencephalogram (EEG)
- 4.2.3.2
- elitism
- 6.4.2
| 6.4.2
- EM algorithm
- 11.4.2
- extensions
- 5.1.3
| 5.4
- EM algorithm,
- extensions
- 5.4.3.2
- EM mapping
- 5.2.2
| 5.2.4
- embarrassingly parallel
- 8.2.2.3
- empirical measure
- 9.1.3
- encapsulation
- 13.2
- encoding
- 6.4.2
- entropy
- 2.6
| 14.2.1
- equidissection
- 2.4.2
- equidistribution
- 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
- equivariance
- 9.2.1
| 9.3.1
- ergodic chain
- 3.2.1
- estimation vs. testing
- 11.2.3
- estimator
- harmonic mean
- 11.3.3
- maximum a posteriori (MAP)
- 11.2.3
- Euler's constant
- 12.1.2
- evolution strategies
- 6.4.1
- evolutionary computation
- 6.4.1
- exact distance
- 6.3.2.3
- excess kurtosis
- 2.3
| 2.3.4
- expectation-conditional maximization (ECM) algorithm
- 5.4.2
| 5.5.2
- multicycle ECM
- 5.4.2.1
| 5.4.2.1
- expectation-conditional maximization either (ECME) algorithm
- 5.4.2.2
| 5.4.3.1
| 5.5.2
- expected shortfall (ES)
- 1.1
- expected tail loss (ETL)
- 1.1
- EXPLOR4
- 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
- exploratory data analysis (EDA)
- 10.1
| 13.1
- exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA)
- 10.6.1
- ExplorN
- 10.3.6
| 10.4
| 10.4
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.5.2
- exponential density function
- 12.1.2
- exponential distribution
- 9.2.7
| 12.1.2
| 12.1.2
- exponential family
- 5.2.1
| 5.2.1
| 5.3.2
| 5.3.2
| 7.1
| 7.2.1
| 7.3.1
| 11.2.1
- sufficient statistics
- 5.2.1
| 5.4.2.2
- Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- 11.2
- extreme value distribution
- 2.2.3.1
- factor analysis model
- 5.4.2.2
- failure-time data
- censored
- 5.1.3
| 5.3.2
- exponential distribution
- 5.3.2
- false discovery rate (FDR)
- 4.4.2.2
- fat-shattering dimension
- 15.2.3
- fault detection
- 6.3.3
- feedforward network
- 13.5.1.2
- filter
- high-pass
- Orthogonality.
- quadrature mirror
- Orthogonality.
- final prediction error (FPE)
- 1.3
- finite mixture
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
- model
- 2.1
| 2.4
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.2
- of Gaussian densities
- 2.3.2.3
- finite-difference SA (FDSA)
- 6.3.2
- Fisher consistent
- 9.1.2
- Fisher information
- 12.4.2
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.3.5
- Fisher scoring algorithm
- 7.3.3
- fitness function
- 6.4.1
| 6.4.2
- fitness proportionate selection
- 6.4.2
- Fitts forecasting model
- 12.3.5
- floating-point
- 6.4.2
- focusing
- 10.3.3
- font
- 12.3.7
- fork-join
- 8.2.1.1
- Fourier plot
- 11.9.2
- Fourier space
- 4.3.2
- Fourier transform
- 4.3.2
- Fréchet differentiable
- 9.2.5
| 9.3.2
| 9.3.4
- free-induction decay (FID) signal
- 4.2.1
- frequency domain bootstrap
- 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
- frequency polygon
- 4.3.3
- Friedman's index
- 6.2.2.2.1
- full conditional distributions
- 3.4.1
- full likelihood
- 12.3.3
- full-screen view
- 12.3.5
- Functional Image Analysis Software - Computational Olio (FIASCO)
- 4.4.2.1
| 4.5.1
- functional model
- 5.1
- functional neuroimaging
- 4.2.3.2
- gain sequences
- 6.3.2
- gamma distribution
- 7.2.1
| 12.1.2
| 2.3.5
- GARCH
- 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.1
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2.2
| 2.4.2.2
- Gauss-Jordan elimination
- 4.2.1
- Gauss-Newton method
- 8.2.1.2
- Gauss-Seidel method
- 4.3.3
| 4.3.5.1
- Gaussian quadrature
- 1.5
- Gaussian simulation smoother
- 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
- Gaussian/normal distribution
- 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.3
| 2.2.3.3
| 2.3
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
| 2.4.2.1
- Matrix
- 2.2.1.3
- truncated
- 2.2.1.3
- gene expression data
- 5.5.3.1
- generalized additive model
- 7.5.8
- generalized cross validation
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 1.6
| 5.4.1.1
- generalized degrees of freedom
- 1.2
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
- generalized EM (GEM) algorithm
- 5.2.2
| 5.2.3
| 5.4.2
| 5.4.2.1
- generalized estimating equations (GEE)
- 7.5.7
- generalized feedback shift register (GFSR)
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.5
- generalized linear mixed models (GLMM)
- 5.4.1.1
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.1
- generalized maximum likelihood method
- 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.6
| 12.3.1
- generalized method of moments
- 2.2.1.2.1
- generalized partial linear model
- 7.5.8
- generalized principal components
- 6.3.1
- generalized principal components analysis (GPCA)
- 6.3.1
- genetic algorithm
- 6.4.3
- genetic algorithms
- 6.4
- geographic brushing
- 10.6.1
- Geometric distribution
- 7.2.1
- geometrically ergodic
- 3.2.1
- getter
- 13.2
- GGobi
- 10.4
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| Web
- Gibbs sampling algorithm
- 3.1
- Gibbs sampling/sampler
- 5.5.1
| 5.5.2
| 5.5.2
| 5.5.3.2
| 11.4.2
| 11.4.2
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.2
- griddy-
- 2.4.2.2
| 2.4.2.2
- mixing of
- 11.4.2
- Givens rotations
- 4.1.3.2
- Glivenko-Cantelli theorem
- 9.1.3
- global optimization
- 6.3.1
| 6.4.1
- global solutions
- 6.1.4
- goodness of fit
- 2.2.3
| 1.1
| 1.2
| 5.3
| 5.4.2.2
- gradient approximation
- 6.3.2
| 6.3.3
- Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization
- 4.1.3.4
- grand tour
- 10.3.5
| 10.3.7
| 10.3.9
- graphics algebra
- 11.3
- Green's algorithm
- 11.4.3
- Greenwood's formula
- 12.1.1
- gross error model
- 9.3.3
- gross error neighbourhood
- 9.2.4
| 9.4.3
- Gumbel distribution
- 2.2.3.1
- Gustafson's law
- 8.2.2.2
- Hall's index
- 6.2.2.2.3
- Halton sequences
- 2.2.3.2.1
- Hampel identifier
- 9.2.7
- hard thresholding
- 1.1
- harmonic mean
- 11.3.3
- hat function
- 2.8.4
- hat matrix
- 5.3.3
- Hawkes process
- 2.3.5
- hazard function
- 12.1
| 12.4.1
| 2.3.5
- hazard rate
- 12.1
- head motion
- 4.4.2.1
| 4.4.2.1
| 4.4.2.1
- Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
- 7.2.2
- Hessian (or Jacobian) matrix
- 6.3.3
- Hessian (second derivative) matrix
- 6.3.1
- heterogeneity
- 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.5
- heterogeneous populations
- 11.2.3
| 11.4.2
- heteroscedasticity
- 1.6
- hexagonal bins
- 4.2.1
- hidden Markov model
- 5.2.3
| 5.5.3.2
| 5.5.3.2
- hierarchical Bayes
- 2.2.3.2.2
- hierarchical command sequence
- 12.3.8
- high breakdown affine equivariant location and scale functionals
- 9.3.4
- high breakdown regression functional
- 9.4.4
- higher-order kernels
- Rates
- highest possible breakdown point
- 9.2.4
- highest posterior region
- 11.2.2
- Householder reflections
- 4.1.3.1
- HPF (High Performance Fortran)
- 8.3.6
- Huber distribution
- 9.1.2
- hue brushing
- 10.3.10
- human-machine interaction
- 6.3.3
- HyperVision
- 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
| 10.4.2
- hypotheses
- 11.2.1
- hypothesis testing
- 5.4.2.2
- i.i.d. resampling
- 2.1
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.7
- identifiability
- 11.2.1
- identification
- 2.2.1.3
| 2.4.1
- problem
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.2
| 2.4.2.2
- restrictions
- 2.2.1.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.1
- Image Analysis
- 5.5.3.2
- image grand tour (IGT)
- 10.3.8
- image registration
- 4.4.2.1
- immersive projection technology (IPT)
- 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
- importance function
- 11.3.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
- choice of
- 11.3.1
- with finite variance
- 11.3.1
- importance sampling
- 3.3
| 1.5
| 3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
- and regular Monte Carlo
- 11.3.2
- degeneracy of
- 11.3.2
| 11.5.2
- efficient (EIS)
- 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
- for model choice
- 11.3.3
- incomplete-data
- likelihood
- 5.1.2
| 5.2.1
- missing data
- 5.1.1
| 5.1.2
| 5.2.1
| 5.3.1
| 5.3.3
| 5.3.5
| 5.4.1.1
| 5.5.3.2
- problem
- 5.1.1
| 5.1.2
| 5.3.1
| 5.5.2
- incremental EM (IEM) algorithm
- 5.4.3.2
- independence M-H
- 3.3
- independence of irrelevant alternatives (IIA)
- 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.1
- independent increments
- 12.4.1
- indexed search
- 2.8.1
- inefficiency factor
- 3.2.2
- infinite collection of models
- 11.2.3
- influence function
- 9.1.2
- information criterion
- Akaike
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.4
| 7.3.5
| 8.1.3.1
| 11.2.3
| 15.2.2.1
- Bayesian
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.5
| 7.3.5
- Schwarz
- 8.1.3.1
- information matrix
- complete-data
- 5.3.5
- expected
- 5.3.5
| 5.3.5
- observed
- 5.3.5
| 5.3.5
- inheritance
- 13.4
| 13.4.4
- injected randomness
- 6.1.3
- instance
- 13.2.3
- integral
- 2.1
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.2
- approximation
- 11.3.1
- high dimensional
- 2.2.1.2.2
- multiple
- 2.3.2
- ratio
- 11.2.2
- integrated mean square error
- No
- intensity
- function
- 2.3.5
- model
- 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
- intensity functions
- 12.4.1
- inter arrival time
- 5.4
| 5.4
| 5.4
| 5.4
| 5.4
- interaction term
- 7.4
- interface
- 13.2.1
| 13.5
| 13.5.4
- interface for derivation
- 13.2.5
- Interface Symposia
- 1.2.2
- International Association for Statistical Computing (IASC)
- 1.2.2
- internet protocol
- 5.2
- intersection classifier
- 5.6
| 5.6
| 5.6
- intersection graph
- 5.6
| 5.6
- invariant
- 3.2
- Inverse Gaussian distribution
- 7.2.1
- inverse iterations
- 4.4.6
- inverse moments
- 6.3.3
- inversion method
- 2.1
| 2.8.1
- inverted gamma density/prior
- 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.4.2.1
- inverted Wishart distribution
- 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.2.2
- iterative refinement
- 4.2.2
- iterative simulation algorithms
- 5.5.2
- iteratively reweighted least squares
- 7.3
| 7.3.3
- Jacobi method
- 4.3.2
| 4.4.2
- Jasp
- Web
- Java threads
- 8.3.2.2
- k-space
- 4.3.2
| 4.3.2
| 4.5.1
- Kalman filter
- 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.5
- augmented
- 2.3.2.3
- Kaplan-Meier curves
- 14.5.1
- Kaplan-Meier method
- 12.1.1
- Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) condition
- 15.5.1.3
- kernel
- function
- 15.4
- kernel trick
- 15.4.1
- matrix
- 15.4.2
- mercer
- 15.4.2.2
- kernel density
- 5.4
| 5.4
| 5.4
| 5.4
- kernel density estimation
- 2.8.3
| 10.3.10
- kernel estimation
- 4.3.4
| 2.3.3
- kernel smoother
- 5.2.1
- keystroke timings
- 5.6
| 5.6
- knowledge discovery
- 13.1
- Kolmogoroff metric
- 9.1.2
| 9.1.3
| 9.2.4
- kriging
- 3.1
| 3.4.1
| 3.5
- Kuiper metric
- 9.2.4
- Kullback-Leibler discrepancy
- 1.3
- lagged-Fibonacci generator
- 2.3.2
- Lagrange multipliers
- 6.2.1
- Laplace approximation
- 1.5
- largest nonidentifiable outlier
- 9.2.7
- Larmor frequency
- 4.2.1
| 4.2.1
- lasso
- 8.1.8
- computation
- 8.1.8
- late binding
- 13.5.1
- latent variables
- 3.1.1
- Latin hypercube sampling
- 3.5.2
- lattice
- 2.3.2
| 2.4.3
| 2.6
- Law of Large Numbers
- 11.3.1
- learning
- 15.1
| 15.2.1
- least median of squares LMS
- 9.4.4
- least squares
- 8.1.1
- computation
- 8.1.1.1
- explicit form
- 8.1.1
- Gauss-Markov theorem
- 8.1.1
- inference
- 8.1.1.2
- orthogonal transformations
- 8.1.1.1
- least trimmed squares
- 9.4.4
| 9.4.5
- length of the shortest half
- 9.2.4
- Levenberg-Marquardt method
- 8.2.1.3
- leverage effect
- 2.3.4
- leverage point
- 9.4.5
| 9.4.5
- library
- 12.3.8
- likelihood
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
- function
- 2.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
| 2.4.1
- intensity-based
- 2.3.5
- intractable
- 11.2
- marginal
- 2.4.2.2
- maximum
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.3.2
| 2.4.1
- simulated
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
- likelihood ratio test
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.3.5
- likelihood smoothing
- 5.5.2
- limited dependent variable
- 2.1
| 2.2
- linear congruential generator (LCG)
- 2.3.1
| 2.3.6
| 2.6
- linear discriminant analysis
- 14.1
- linear feedback shift register (LFSR)
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.6
| 2.6
- linear recurrence
- 2.3.1
- linear recurrence modulo 2
- 2.4.1
- linear recurrence with carry
- 2.3.6
- linear reduction
- 6.2
- linear regression
- 7.1
| 8.
| 8.1
| 8.1
| 9.4.1
- linear smoother
- 5.2.1
| 5.3
- linear system
- direct methods
- 4.2
- Gauss-Jordan elimination
- 4.2.1
- iterative refinement
- 4.2.2
- gradient methods
- 4.3.5
- conjugate gradient method
- 4.3.5.3
- Gauss-Seidel method
- 4.3.5.1
- steepest descent method
- 4.3.5.2
- iterative methods
- 4.3
- Gauss-Seidel method
- 4.3.3
- general principle
- 4.3.1
- Jacobi method
- 4.3.2
- successive overrelaxation (SOR) method
- 4.3.4
- link function
- 5.5.2.1
| 7.1
| 7.2.2
| 11.3.3
- canonical
- 7.2.2
- linked brushing
- 10.3.2
- linked highlighting
- 13.5.2.3
- linked views
- 10.3.2
- linking
- 12.3.5
- local bootstrap
- 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
- local likelihood
- 5.5.2.1
- local likelihood equations
- 5.5.2.1
- local linear estimate
- 5.2.2
| 5.2.2
- local optimization
- 6.3.1
- local polynomial
- 5.3
| 5.5.2.1
- local regression
- 5.2.2
- local reversibility
- 3.3.3
- localized random search
- 6.2.2.2
| 6.3.2
- location functional
- 9.1.2
| 9.2.1
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.5
| 9.3.1
| 9.3.4
- location-scale-free transformation
- 12.2
- log-likelihood
- 3.3.2.1
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.3.1
- log-linear model
- 7.5.5
| 12.4.2
- log-logistic distribution
- 12.1.2
- log-normal distribution
- 12.1.2
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.3.5
- log-rank statistic
- 14.5.1
- logistic distribution
- 2.2.3.1
- logit
- 7.2.1
- mixed
- 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.4
- mixed multinomial (MMNL)
- 2.2
| 2.2.3
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.2.3.3
- model
- 2.2.3.1
| 2.4
- multinomial
- 2.2.3.1
- probability
- 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
- logit model
- 7.1
| 7.2.2
| 7.4
- longitudinal
- 3.8.2
- longitudinal data
- 7.5.7
- loss function
- 6.1.1
| 15.2.1
- low pass filter
- 1.1
- LR method
- 4.4.5
- LU decomposition
- 4.1.2
- M-estimation
- 5.5.3.1
- M-functional
- 9.2.3
| 9.2.3
| 9.2.3
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.5
| 9.2.6
| 9.2.6
| 9.3.2
| 9.3.2
| 9.3.2
| 9.4.2
| 9.4.3
- with a redescending
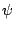 -function
-function
- 9.2.3
- M-step (Maximization step)
- 5.1.2
| 5.2.1
- exponential family
- 5.2.1
| 5.3.2
- factor analysis model
- 5.4.2.2
- failure-time data
- 5.3.2
- generalized EM (GEM) algorithm
- 5.2.2
- normal mixtures
- 5.3.1
- magnetic field inhomogeneities
- 4.3.3.1
| 4.4.2.1
- magnetic resonance
- 4.2.1
- magnetic resonance imaging
- 4.2.2
- magnetism
- 4.2.1
- magnetoencephalogram (MEG)
- 4.2.3.2
- Mallow Cp
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.4
| 1.4
- MANET
- 10.4
| 10.4
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
- margin
- 15.3.2
- marginal distribution function
- 12.2
- marginal likelihood
- 3.1
- market risk
- 1.1
- marketing
- 2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
- Markov bootstrap
- 2.4
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.7
- Markov chain
- 3.1
| 3.2.1
| 6.4.5
- Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
- 3.1
| 5.5.1
| 5.5.2
| 1.5
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.1
- Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm
- 11.1
| 11.4
| 11.4
- automated
- 11.5.1
- Markov random field
- 5.5.3.2
- Markov switching autoregressive model
- 2.4.2
| 2.4.2.1
- masking effect
- 9.2.7
- Mason Hypergraphics
- 10.5.1
- Mathematica
- Web
- mathematical programming
- 6.3.1
- matrix decompositions
- 4.1
- Cholesky decomposition
- 4.1.1
- Givens rotations
- 4.1.3.2
- Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization
- 4.1.3.4
- Householder reflections
- 4.1.3.1
- LU decomposition
- 4.1.2
- QR decomposition
- 4.1.3
- SVD decomposition
- 4.1.4
- matrix inversion
- 4.1.5
- matrix linear recurrence
- 2.4.1
- maximally equidistributed
- 2.4.2
| 2.4.6
- maximum full likelihood
- 12.3.3
- maximum likelihood
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.3.2
| 2.4.1
- Monte Carlo (MCML)
- 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
- quasi- (QML)
- 2.3.5
- simulated
- 2.2.1.2.1
- maximum likelihood estimate
- 9.2.3
| 12.1.2
- maximum likelihood estimation
- 5.1.1
- global maximum
- 5.1.1
| 5.2.3
| 5.2.3
- local maxima
- 5.1.1
| 5.2.3
| 5.2.3
| 5.3.4
- maximum partial likelihood
- 12.3.3
- maximum score method
- 10.4
- maximum-likelihood
- 7.3
| 7.3.2
- mean squared error
- 6.3.3
| 1.2
| No
| 5.3
- measurement noise
- 6.3.2
- median
- 9.1.1
| 9.1.2
| 9.2.2
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.7
| 9.3.1
| 9.5.1
| 9.5.2
- median absolute deviation MAD
- 9.1.1
| 9.2.2
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.7
| 9.5.1
- median polish
- 9.5.2
- menu hierarchy
- 12.3.3
- Mersenne twister
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
| 2.7
- message
- 13.2.2
- metaclass
- 13.2.3.1
- metamodel
- 3.1
| 3.3
| 3.3
| 3.4.1
| 3.5.1
- method of composition
- 3.8.1
- method of moments
- 12.1.2
- Metropolis Hastings (MH) algorithm
- 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
- Metropolis method
- 3.1
- Metropolis-Hastings agorithm
- 11.4
- Metropolis-Hastings algorithm
- 5.5.2
| 11.4.1
| 2.2.3.2.2
- Metropolis-Hastings method
- 3.1
- micromaps
- 10.6.2
- military conscripts
- 11.4.2
- MIMD (multiple instruction stream-multiple data stream)
- 8.2
- MiniCAVE
- 10.5.2
- minimum covariance determinant (MCD)
- 9.3.4
- minimum volume ellipsoid (MVE)
- 9.3.4
- mirror filter
- 7.4.1
- misclassification cost
- 14.2.2
- missing variables
- simulation of
- 11.4.2
- mixed model
- 7.5.7
- mixed multinomial logit (MMNL)
- 2.2
| 2.2.3
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.2.3.3
- mixing
- 3.1.1
- mixing density/distribution
- 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.3
| 2.2.3.3
- mixture
- Poisson distributions
- 11.2.3
- mixture models
- 5.1.1
| 5.3.4
| 5.5.1
- mixture of factor analyzers
- 5.4.2.2
| 5.5.3.1
- normal mixtures
- 5.3.1
| 5.3.5
| 5.4.3.2
| 5.4.3.2
| 5.4.3.2
- Mixture Sampler algorithm
- 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
- mode
- attraction
- 11.4.1
- mode tree
- 4.3.4
- model
- AR
- 11.2.1
| 11.2.3
| 11.4.3
- averaging
- 11.2.3
| 11.4.3
- binomial
- 11.2.2
- choice
- 11.4.3
- generalised linear
- 11.2.1
- generalized linear
- 11.3.3
- index
- 11.4.3
- mixture
- 11.4.2
- probit
- 11.3.2
| 11.4.1
- model averaging
- 11.2.3
- model choice
- 11.2.3
- and testing
- 11.2.3
- parameter space
- 11.2.3
- model complexity
- 1.1
- model domain
- 13.1.1
- model selection
- 1.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.1
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.3.5
- modified Bessel function
- 1.3
- moment generating function
- 7.1
- moment index
- 6.2.2.2.2
- Mondrian
- 10.4
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
- Monte Carlo
- 6.1.3
- confidence interval
- 11.3.2
- Markov chain (MCMC)
- 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.1
- maximum likelihood (MCML)
- 2.3.2
- with importance function
- 11.3.1
- Monte Carlo EM
- 5.4.1
| 5.4.1.1
| 5.5.2
- Monte Carlo maximum likelihood (MCML)
- 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
- Monte Carlo method
- 2.1
| 13.1.1
| 3.1
| 3.1
| 3.2
| 11.3.1
- and the curse of dimension
- 11.3.2
- Monte Carlo techniques
- 11.3
- efficiency of
- 11.3.2
- population
- 11.5.2
- sequential
- 11.5.2
- Moore's law
- 8.1
- mosaic map
- 4.2.1
- mosaic plot
- 10.3.11
| 13.5.2.3
- mother wavelet
- Orthogonality.
- MPI (Message Passing Interface)
- 8.3.5
- multicollinearity
- 8.1.2
| 8.1.2
- exact
- 8.1.2
| 8.1.2
- near
- 8.1.2
| 8.1.2
- multilevel model
- 7.5.7
- multimodality
- 2.4.2.1
- multinomial distribution
- 2.4.2.2
- multinomial responses
- 7.5.4
- multiple binary responses
- 14.6
- multiple counting processes
- 12.4.2
- multiple document interface
- 12.3.5
- multiple failures
- 12.4
| 12.4.1
- multiple recursive generator (MRG)
- 2.3.1
- multiple recursive matrix generator
- 2.4.5
- multiple-block M-H algorithms
- 3.1
- multiply-with-carry generator
- 2.3.6
- multiresolution analysis
- 7.3.3
- multiresolution analysis (MRA)
- 7.3.3
- multiresolution kd-trees
- 5.4.3.2
- multivariate smoothing
- 5.5
- multivariate-t density
- 3.3.2.2
- mutation
- 6.4.2
| 6.4.2
- Nadaraya-Watson estimate
- 2.2
| 5.2.1
- negative binomial distribution
- 7.2.1
- nested models
- 7.3.5
- network sensor
- 5.3
- neural network
- 6.3.3
| 13.5.1.2
| 15.4.1
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
- 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
- Newton's method
- 6.3.1
| 8.2.1.1
- Newton-Raphson algorithm
- 6.3.1
| 6.3.3
| 7.3.3
| 2.2.3.2.1
- Newton-Raphson method
- 5.5.2.2
| 12.4.2
- Neyman-Pearson theory
- 11.2.2
- no free lunch (NFL) theorems
- 6.1.4
- node impurity
- 14.2.1
- noisy measurement
- Convergence
| 6.3.1
- nominal logistic regression
- 7.5.4
- non-nested models
- 7.3.5
- nonhomogeneous Poisson process
- 12.4.2
| 12.4.4
- nonlinear least squares
- 8.2.1
| 8.2.1
- asymptotic normality
- 8.2.1
- inference
- 8.2.2
- nonlinear regression
- 8.
| 8.2
- nonparametric autoregressive bootstrap
- 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.4
- nonparametric curve estimation
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.4.7
- nonparametric density estimation
- 4.1
- normal approximation
- 11.3.2
- normal distribution
- 9.1.1
| 9.2.6
- normal equations
- 5.2.2
| 8.1.1
- normalization property
- 7.3.5
- normalizing constant
- 11.3.1
| 11.3.3
- ratios of
- 11.3.3
- novelty detection
- 15.1
| 15.6.2
- NOW (network of workstations)
- 8.2.1.2
- nuisance parameter
- 12.4.2
| 12.4.4
- null deviance
- 7.4
- NUMA (non-uniform memory access)
- 8.2.1.1
- numerical standard error
- 3.2.2
- nViZn
- 10.6.2
- Nyquist ghosts
- 4.3.3.1
| 4.4.2.1
- object
- 13.2
- object composition
- 13.2.4
| 13.4.4
- Object oriented programming (OOP)
- 13.1
- object, starting
- 13.7
- Occam's razor
- 1.2
| 1.5
- offset
- 7.3.4
- Old Faithful geyser data
- 4.2.1
| 4.2.1
- one-way analysis of variance
- 9.5.1
- one-way table
- 9.5.1
- OpenMP
- 8.3.3
- optimization/optimizer
- 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.3
| 2.4.1
- order of menu items
- 12.3.3
- ordered probit model
- 7.5.4
- ordinal logistic regression
- 7.5.4
- ordinary least squares (OLS)
- 2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
- orthogonal series
- 5.2.5
- outlier
- 9.1.1
| 9.2.3
| 9.2.6
| 9.2.7
| 9.3.5
| 9.4.3
| 9.5.2
| 2.3.4
- outlier detection
- 15.1
| 15.6.2
- outlier identification
- 9.3.5
| 9.5.1
- outlier region
- 9.2.7
- outwards testing
- 9.2.7
- overdispersion
- 7.5.2
- overfitting
- 13.5.1.1
- oversmoothing
- Choosing
| 4.3.2
| 4.3.3
- panel data
- 7.5.7
| 2.2
| 2.4.2.2
- panning
- 10.3.3
- parallel computing
- 8.1
- parallel coordinate display
- 10.3.6
- parallel coordinate plot
- 10.3.6
| 11.9.2
- parallel coordinates
- 13.5.2.2
| 5.5
| 5.5
| 5.5
- parameter
- of interest
- 11.2.1
- parameter space
- constrained
- 11.2
- parameter-expanded EM (PX-EM) algorithm
- 5.4.3.1
- Parseval formula
- 7.2.4
- partial autocorrelation
- 11.2.1
- partial least squares
- 8.1.9
- algorithm
- 8.1.9
- extensions
- 8.1.9
- latent variables
- 8.1.9
- modified Wold's R
- 8.1.9
- nonlinear regression
- 8.2.3
- Wold's R
- 8.1.9
- partial likelihood
- 12.3.1
| 12.3.3
- partially linear models
- 10.2.2
- particle systems
- 11.5.2
- password cracking
- 5.6
- pattern recognition
- 6.3.3
- Pearson statistic
- 7.3.4
- penalized least squares
- 1.1
| 5.2.3
- penalized likelihood
- 5.1.1
| 5.4.3.1
| 5.5.3.2
| 5.5.2
- perfect sampling method
- 3.9
- periodogram
- 7.2.1
- permutation tests
- 2.3
| 2.3
- physiological noise
- 4.3.3.2
| 4.4.2.1
- pie chart
- 10.3.11
- piecewise polynomial
- 5.2.4
- pilot estimate
- 5.4.1.3
- pixel grand tour
- 10.3.8
- plug-in
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
- plug-in bandwidth selection
- 5.4.1.3
- PMC vs. MCMC
- 11.5.2
- point process
- 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
- Poisson data
- 7.2
- Poisson distribution
- 2.6
| 12.4.1
| 2.4.1
- Poisson process
- 2.8.5
- polymorphic class
- 13.5.1
- polymorphism
- 13.5
- polynomial lattice
- 2.4.3
- polynomial LCG
- 2.4.4
- polynomial regression
- 3.1
| 3.4.3
| 3.6
- polynomial terms
- 7.4
- population
- 6.4.1
- population Monte Carlo (PMC) techniques
- 11.5.2
- positron emission tomography (PET)
- 4.2.3.2
- posterior density
- 3.3.2
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.4.2.1
- posterior distribution
- 11.2.1
- posterior mean
- 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.4
| 2.4.2.1
| 2.4.2.1
- posterior probability
- 5.3.1
| 5.3.4
| 5.4.3.2
- power expansions
- 12.3.3
- power method
- 4.4.1
- power parameter
- 12.2
- prediction
- 5.4.1.1
| 5.4.1.1
| 11.2.1
- sequential
- 11.2.1
- predictive modeling
- 13.4.3
- predictive squared error
- 1.2
- PRESS
- 1.4
- primitive polynomial
- 2.3.1
| 2.4.1
- principal components analysis (PCA)
- 6.2.1
| 8.1.4
- principal components regression
- 8.1.4
| 8.1.4
- choice of principle components
- 8.1.4
| 8.1.4
- principal curve
- 6.3.3
- prior
- proper
- 11.3.1
- prior (density)
- 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2.2
- informative
- 2.4.2.2
- uninformative
- 2.2.1.3
| 2.3.2.3
- prior distribution
- 11.2
- conjugate
- 11.2.1
- selection of a
- 11.2
- prior-posterior summary
- 3.3.2.1
- probability of move
- 3.1
- probit
- model
- 2.2.3.1
| 2.4.1
- multinomial
- 2.2.1.3
- multinomial multiperiod
- 2.2
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.2
- multivariate
- 2.2
| 2.2.1
| 2.2.2
- static multinomial
- 2.2.1.3
- probit model
- 7.2.2
| 7.4
- probit regression
- 3.5
- problem domain
- 13.1.1
- process control
- 6.3.3
- process forking
- 8.3.1
- productivity
- 12.3.6
- program execution profiling
- 5.6
- progress bar
- 12.3.6
- projection
- 10.3.4
- projection index
- 6.2.2
- projection pursuit
- 10.3.7
| 5.5
| 6.2.2
- projection pursuit guided tour
- 10.3.7
- projection pursuit index
- 10.3.7
- projection step
- 6.3.3.1
- proportion
- 6.2.1.1
- proportional hazard
- 14.5.1
- proportional hazards model
- 10.3
| 12.3.3
- proposal
- adaptive
- 11.5.2
- multiscale
- 11.5.2
- proposal distribution
- 3.1
- prosection matrix
- 10.3.3
- prosections
- 10.3.3
- proximity
- 14.3.3
- pruning
- 13.5.1.1
- pseudo data
- 2.1
- pseudo-likelihood
- 7.5.3
- pseudorandom number generator
- 2.1
- Pthread library
- 8.3.2.1
- pulse sequence
- 4.3.1
- PVM (Parallel Virtual Machine)
- 8.3.4
- QR decomposition
- 4.1.3
- QR method
- 4.4.4
- quadratic principal components analysis (QPCA)
- 6.3.1
- quality improvement
- 6.3.3
- quantlets
- CSAfin06
- 1.2.5
- quasi-likelihood
- 7.5.3
- quasi-maximum likelihood (QML)
- 2.3.5
- queuing systems
- 6.3.3
- R
- Web
| 11.6
- radial basis networks
- 15.4.1
- random effects
- 3.8.2
| 5.4.1.1
| 5.4.1.1
- random forests
- 14.3.3
- random graph
- 5.6
- random noise
- 6.1.3
- random number generator
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 13.2.4
- approximate factoring
- 2.3.3
- combined generators
- 2.3.4
| 2.4.6
| 2.5
| 2.7
- definition
- 2.2.2
- figure of merit
- 2.3.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.4.2
- floating-point implementation
- 2.3.3
- implementation
- 2.3.3
| 2.5
- jumping ahead
- 2.2.3
| 2.3.5
| 2.4.1
- non-uniform
- 2.8
- nonlinear
- 2.5
- period length
- 2.2.2
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.5
- physical device
- 2.2.1
- power-of-two modulus
- 2.3.3
- powers-of-two-decomposition
- 2.3.3
- purely periodic
- 2.2.2
- quality criteria
- 2.2.3
| 2.8
- seed
- 2.2.2
- state
- 2.2.2
- statistical tests
- 2.2.4
| 2.6
- streams and substreams
- 2.2.3
| 2.7
- random numbers
- 13.2.4
- common
- 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.3.2.1
- pseudo-
- 2.2.3.2.1
- quasi-
- 2.2.3.2.1
- random permutation
- 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.3
- random permutation sampler
- 2.4.2.1
- random perturbation vector
- 6.3.3
- random search
- 6.2
- random walk M-H
- 3.3
- Rao-Blackwellization
- 3.6
- rate of convergence
- 5.2.4
| 5.3.5
| 5.4.2.1
| 5.4.2.2
| 5.4.3.2
| 5.4.3.2
- rate matrix
- 5.2.4
- ratio
- and normalizing constants
- 11.3.1
- importance sampling for
- 11.3.3
- of integrals
- 11.3.2
- of posterior probabilities
- 11.2.2
- ratio-of-uniforms method
- 2.8.6
- real-number coding
- 6.4.2
- recursive partitioning
- 11.9.3
- recursive sample mean
- 5.4
- red-green blindness
- 12.3.7
- reduced conditional ordinates
- 3.6
- reformatting
- 10.3.3
- REGARD
- 10.4
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.6.1
- regression depth
- 9.4.4
- regression equivariant
- 9.4.2
- regression functional
- 9.4.1
- regression splines
- 5.2.4
- regression trees
- 14.7
- regression-type bootstrap
- 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
- regressor-outlier
- 9.4.5
- regularization
- 15.2.2.1
| 15.2.2.1
- rejection method
- 2.8.4
| 2.8.6
- rejection sampling
- 2.3.2.3
- relative projection Pursuit
- 6.2.2.3
- remote sensing data
- 4.2.1
- resampling
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 5.4.3
- resampling tests
- 2.2
| 2.3
- rescaling
- 10.3.3
- residual
- 9.5.2
- residual sum of squares
- 7.3.2
- residuals
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.3.4
- resistant one-step identifier
- 9.4.5
- resolution of identity
- Resolution
- response-outlier
- 9.4.5
- restricted maximum likelihood
- 1.5
- reverse move,
- probability
- 11.4.3
- reversible
- 3.2.1
- reversible jump MCMC
- 11.4.3
| 11.4.3
- ridge regression
- 11.2
| 8.1.6
| 8.1.6
- almost unbiased
- 8.1.6.2
- almost unbiased feasible
- 8.1.6.2
- bias
- 8.1.6
- choice of ridge parameter
- 8.1.6
| 8.1.6.1
| 8.1.6.1
- feasible generalized
- 8.1.6.1
- generalized
- 8.1.6.1
- minimization formulation
- 8.1.6
- nonlinear regression
- 8.2.3
- reduced-rank data
- 8.1.6.3
- risk
- 15.2.1
- empirical
- 15.2.2
| 15.2.2
- expected
- 15.2.2
- regularized
- 15.2.2.1
- structural minimization
- 15.2.3
- risk measure
- 1.1
| 1.1
- Robbin-Monro algorithm
- 11.5.1
- robust
- 9.4.2
- robust functional
- 9.2.7
- robust location functional
- 9.1.3
- robust regression
- 5.5.3
| 5.5.3.1
| 9.4.1
| 9.4.3
- robust scatter functional
- 9.3.4
- robust statistic
- 9.1.1
| 9.1.2
| 9.1.3
- robustness
- 9.1.2
| 9.2.2
| 9.2.4
- root node
- 14.2.1
- root-finding
- 6.1.1
| 6.3.2
- rotation
- 10.3.4
- roulette wheel selection
- 6.4.2
- S-functional
- 9.2.3
| 9.3.4
| 9.3.5
| 9.4.4
| 9.4.5
- S-Plus
- Web
- sample mean
- 12.1.2
- sampler performance
- 3.1.1
- SAS
- Web
- Satterwaite approximation
- 5.4.2.2
- saturated model
- 7.3.2
- saturation brushing
- 10.3.10
- scalable EM algorithm
- 5.4.3.2
- scale functional
- 9.2.1
| 9.2.4
- scales
- 11.4
- scaling algorithm
- 11.4.1
- scaling equation
- 7.3.3
- scaling function
- 7.3.3
- scanner data
- 2.2.1.3
- scatter diagram
- 4.2.1
| 4.2.1
- scatterplot
- 10.3.1
| 12.3.5
- scatterplot matrix
- 10.3.1
| 12.3.5
| 12.3.5
- schema theory
- 6.4.5
- search direction
- 6.1.3
- secondary data analysis
- 13.2
- selection
- 6.4.2
| 6.4.2
- selection sequences
- 10.3.2
- self-consistency
- 5.2.3
- semiparametric models
- 5.5
| 10.2
- semiparametric regression
- 7.5.8
- sensitivity analysis
- 3.1
- sensor placement
- 6.3.3
- serial test
- 2.6
- setter
- 13.2
- shape parameter
- 12.1.2
- shared memory
- 8.2.1
- shortcut
- 12.3.3
- shortest half
- 9.1.3
| 9.2.3
| 9.3.4
| 9.4.4
- shrinkage estimation
- 8.1.5
- shrinking neighbourhood
- 9.1.2
- sieve bootstrap
- 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
- SIMD (single instruction stream-multiple data stream)
- 8.2
- simulated maximum likelihood (SML)
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
| 2.2.3.3
| 2.2.3.3
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
- quasi-random
- 2.2.3.2.1
- simulated moments
- 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.1
- simulated scores
- 2.2.3.2.1
- simulated tempering
- 3.8.3
- simulation
- 3.1
| 3.1
| 3.2
| 3.4.2
| 3.4.4
| 3.6
| 11.3
| 11.3.1
| 2.1
| 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.1.2.1
| 2.2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
| 2.3.5
| 2.4.2.2
- simulation-based optimization
- 6.1.3
| 6.3.3
- simultaneous perturbation SA (SPSA)
- 6.3.3
- single index model
- 7.5.8
| 10.2.1
- single trial fMRI
- 4.3.1
- SISD (single instruction stream-single data stream)
- 8.2
- slammer worm
- 5.7
- slash distribution
- 9.2.6
- slice sampling
- 3.5
- sliced inverse regression
- 6.4.1
- slicing
- 10.3.3
- smooth bootstrap
- 11.5.2
- smoothed maximum score
- 10.4
- smoothing
- 5.1
- smoothing parameter
- 1.1
| 1.3
| 1.5
| 1.6
| Smoothing
| 5.3
- SMP (symmetric multiprocessor)
- 8.2.1.1
- soft thresholding
- 1.1
- software reliability
- 12.4
- sparse matrices
- 4.5
- sparsity
- 15.5.1.3
- specification search
- 10.1
- spectral density
- 7.2.1
- spectral test
- 2.3.2
- spectrogram
- 7.2.2
- speech recognition
- 14.1
- Spider
- 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
| 10.4.1
- SPIEM algorithm
- 5.4.3.2
- spine plot
- 10.3.11
- spline
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.2.1
| 1.4
| 1.4
- spline smoother
- 5.2.3
| 5.2.4
- spreadplots
- 10.3.11
- SPSA Web site
- 6.3.3
- SPSS
- Web
- SQL
- 11.2
- squeeze function
- 2.8.4
- SRM
- see structural risk minimization
- stably bounded algebraic curve
- 6.3.2.5
- standard deviation
- 9.1.1
| 9.2.2
| 9.2.4
| 9.2.7
- standard errors
- 5.3.5
| 5.3.5
| 5.3.5
- starting (initial) value
- 5.2.3
| 5.2.3
| 5.3.4
| 5.3.4
| 5.3.4
- state space
- 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.3
- state space model
- Gaussian linear
- 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.5
- stationarity
- 11.2.1
| 2.3.1
| 2.4.2.2
- statistical computing
- 1.1
- statistical functional
- 9.1.2
| 9.1.2
- Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM)
- 4.5.1
- steepest descent
- 6.3.1
- steepest descent method
- 4.3.5.2
- Stein-rule estimator
- 8.1.5
- stereoscopic display
- 10.5
- stereoscopic graphic
- 10.5.1
- stochastic approximation
- 6.3
- stochastic conditional duration (SCD) model
- 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
- stochastic gradient
- 6.3.1
- Stochastic optimization
- 6.
- stock trading system
- 2.3.5
- stopping rule
- 11.5.2
- streaming data
- 5.4
- structural risk minimization
- 15.2.3
| 15.2.3
| 15.3.2
- structure parameter
- 12.4.4
- Structured Query Language
- 11.2
- subsampling
- 2.1
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.4
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2
- subtract-with-borrow
- 2.3.6
- successive overrelaxation (SOR) method
- 4.3.4
- supervised learning
- 13.3
- supplemented EM (SEM) algorithm
- 5.3.5
| 5.4
- support
- 13.5.1.4
- support vector machine
- 15.1
- decomposition
- 15.5.2
- linear
- 15.3
- optimization
- 15.5.1
- sequential minimal optimization (SMO)
- 15.5.2.3
- sparsity
- 15.5.1.3
- support vector novelty detection
- 15.6.2
- support vector regression
- 15.6.1
- surrogate data tests
- 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
- surrogate splits
- 14.3.3
- survival analysis
- 5.3.2
- survival function
- 12.1
- survival model
- 5.5.3
| 7.5.6
- survival rate
- variance
- 11.5.2
- survival trees
- 14.5
- susceptibility artifacts
- 4.3.3.2
- SV model
- 2.1
| 2.3
| 2.3.5
- canonical
- 2.3.1
| 2.3.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.2.2
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.4
| 2.3.5
- multivariate
- 2.3.4
- SVD decomposition
- 4.1.4
- symmetric command sequence
- 12.3.8
- syn cookie
- 5.3
- SYSTAT
- Web
- systems of linear equations
- direct methods
- 4.2
- Gauss-Jordan elimination
- 4.2.1
- iterative refinement
- 4.2.2
- gradient methods
- 4.3.5
- conjugate gradient method
- 4.3.5.3
- Gauss-Seidel method
- 4.3.5.1
- steepest descent method
- 4.3.5.2
- iterative methods
- 4.3
- Gauss-Seidel method
- 4.3.3
- general principle
- 4.3.1
- Jacobi method
- 4.3.2
- SOR method
- 4.3.4
- Table Production Language (TPL)
- 11.3.4.1
| 11.3.4.1
- tailored M-H
- 3.3
- tailoring
- 3.3.3
- TAQ database
- 2.3.5
- target tracking
- 6.1.3
- Tausworthe generator
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.4
- Taylor series
- 5.3.1
- Taylor series expansions
- 12.4.2
- TCP three-way handshake
- 5.3
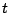 -distribution, folded
-distribution, folded
- 11.3.2
- tempering
- 2.4.5
- terminal nodes
- 14.2.2
- termination criterion
- 6.4.4
- Tesla
- 4.2.1
- thinning
- 2.8.5
- threading
- 8.3.2
- threshold parameters
- 12.1.2
- thresholding
- 7.3.1
- time series
- 2.1
| 2.1
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.3
| 2.4
| 2.4
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.2
| 2.4.3
| 2.4.4
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.6
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.4.7
| 2.1
| 2.3
| 2.4.2.2
| 2.4.2.2
- tissue contrast
- 4.2.2
- tournament selection
- 6.4.2
- traffic management
- 6.3.3
- training data
- 13.3
- transform
- continuous wavelet
- 7.3.2
- discrete Fourier
- 7.2.1
- discrete wavelet
- 7.4
- empirical Fourier-Stieltjes
- 7.1
- fast Fourier
- 7.4
- Fourier-Stieltjes
- 7.1
- Hilbert
- 7.2.3
- integral Fourier
- 7.2.2
- Laplace
- 7.1
- short time Fourier
- 7.2.2
- Wigner-Ville
- 7.2.4
- windowed Fourier
- 7.2.2
- transformation
- Box-Cox
- 7.1
- Fisher
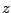
- 7.1
- transformation models
- 10.2.4
- transformed density rejection
- 2.8.4
- transition kernel
- 3.2.1
- transition matrix
- 6.4.5
- translation equivariant functional
- 9.3.3
- transmission control protocol
- 5.2
- trapping state
- 11.4.2
- tree growing
- 14.2.1
- tree pruning
- 14.2.2
- tree repairing
- 14.7
- Trellis display
- 12.3.5
| 12.3.5
- triangular distribution
- 2.2.3.1
- trigonometric regression
- 1.1
| 1.1
| 1.2
| 1.4
| 1.4
- trojan program
- 5.4
| 5.4
- Tukey's biweight function
- 9.2.3
| 9.3.5
- twisted generalized feedback shift register (GFSR)
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.6
- two-way analysis of variance
- 9.5.2
- UMA (uniform memory access)
- 8.2.1.1
- unbiased risk
- 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.3
| 1.6
- unbiased risk estimation
- 5.4.1.2
- under-fitting
- 15.2.2
- Unified Modelling Language (UML)
- 13.1.2
| 13.3
- uniform distribution
- 2.1
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.4.2.2
- uniformity measure
- 2.2.3
| 2.4.2
- unit measurement
- 11.4.2
- unobserved (or latent) variables
- 2.1
- unobserved heterogeneity
- 10.3
- unpredictability
- 2.2.5
- unsupervised learning
- 13.3
- user profiling
- 5.6
- utility/utilities
- 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.1
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.2.2
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.1.3
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.1
| 2.2.3.3
- validation data
- 13.3
- Value at Risk (VaR)
- 1.1
| 1.1
- copulas
- 1.4
- vanGogh
- Web
- vanishing moments
- 7.3.5
- Vapnik-Cervonenkis class
- 9.3.1
- variable
- auxiliary
- 11.4.2
- variable selection
- 1.1
| 8.1.3
- all-subsets regression
- 8.1.3.3
| 8.1.3.3
- branch and bound
- 8.1.3.3
- genetic algorithms
- 8.1.3.3
- backward elimination
- 8.1.3.1
- cross validation
- 8.1.3.4
- forward selection
- 8.1.3.2
- least angle regression
- 8.1.3.2
- stepwise regression
- 8.1.3.1
- variance estimation
- 5.3.3.1
- variance reduction
- 2.8
| 2.8.1
- variance reduction technique
- 3.2
- varset
- 11.2
| 11.2.2
- VC-bound
- 15.2.3
- VC-dimension
- 15.2.3
- VC-theory
- 15.2.3
- vector error-correction model
- 2.2.1.3
- Virtual Data Visualizer
- 10.5.2
- virtual desktop
- 12.3.5
- virtual reality (VR)
- 10.1
| 10.5
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.7.1
- Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML)
- 10.5.2
- visual data mining (VDM)
- 10.1
- volatility of asset returns
- 2.1
| 2.3
- voting
- 2.2
| 2.2.2
- VoxBo
- 4.5.1
- VRGobi
- 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
 -transformation
-transformation
- 12.2
- Wasserstein metrics
- 14.5.1
- waterfall plot
- 5.5
- wavelet domain
- 7.4
- wavelet regularization
- 15.2.2.1
- wavelets
- 7.3
- Daubechies
- 7.3.5
- Haar
- 7.3.4
- Mexican hat
- 7.3.2
- periodized
- 7.4.1
- sombrero
- 7.3.2
- Weibull density function
- 12.1.2
- Weibull distribution
- 12.1.2
| 12.1.2
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
| 2.3.5
- Weibull process model
- 12.4.3
- weight function
- 5.2.1
- weights
- generalized linear model (GLM)
- 7.3.4
| 7.5.1
- wild bootstrap
- 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.5
| 2.4.7
- winBUGS
- 11.1
| 11.6
- window titles
- 5.6
- Wishart distribution
- 2.2.1.3
- working correlation
- 7.5.7
- XGobi
- 10.3.6
| 10.4
| 10.4
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.4.3
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.5.2
| 10.6.1
| 10.6.1
- XML
- 11.2
- XploRe
- Web
| 1.1
| 1.2.2
| 1.3
- zooming
- 10.3.3
 -stable
-stable
 -stable
-stable
 -stable
-stable -stable
-stable parametrization
parametrization
 -stable
-stable parametrization
parametrization
 -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable -stable
-stable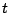
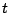
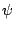 -function
-function