



Next: 4. Numerical Linear Algebra
Up: csahtml
Previous: 3.9 Concluding Remarks
-
- 1
-
Albert, J. and Chib, S. (1993).
Bayesian analysis of binary and polychotomous response data.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88: 669-679.
- 2
-
Besag, J. (1974).
Spatial interaction and the statistical analysis of lattice systems
(withdiscussion).
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 36: 192-236.
- 3
-
Besag, J., Green, E., Higdon, D. and Mengersen, K.L. (1995).
Bayesian Computation and Stochastic Systems (with discussion).
Statistical Science, 10: 3-66.
- 4
-
Best, N.G., Cowles, M.K. and Vines, S.K. (1995).
CODA: Convergence diagnostics and output analysis software for Gibbs sampling.
Technical report, Cambridge MRC Biostatistics Unit.
- 5
-
Carlin, B.P. and Louis, T. (2000).
Bayes and Empirical Bayes Methods for Data Analysis, 2nd ed,
Chapman and Hall, London.
- 6
-
Casella, G. and Robert, C.P. (1996).
Rao-Blackwellization of sampling schemes.
Biometrika, 83: 81-94.
- 7
-
Chan, K.S. (1993).
Asymptotic behavior of the Gibbs sampler.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88: 320-326.
- 8
-
Chan, K.S. and Ledolter, J. (1995).
Monte Carlo EM estimation for time series models involving counts.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90: 242-252.
- 9
-
Chen, M-H. (1994).
Importance-weighted marginal Bayesian posterior density estimation.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89: 818-824.
- 10
-
Chen, M-H., Shao, Qi-M. and Ibrahim, J.G. (2000),
Monte Carlo Methods in Bayesian Computation,
Springer Verlag, New York.
- 11
-
Chib, S. (1995).
Marginal likelihood from the Gibbs output.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90: 1313-1321.
- 12
-
Chib, S. (2001).
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods: Computation and Inference.
In Heckman, J.J. and Leamer, E. (eds), Handbook of Econometrics,
Volume 5, pp. 3569-3649, North Holland, Amsterdam.
- 13
-
Chib, S. and Greenberg, E. (1994).
Bayes inference for regression models with ARMA
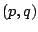 errors.
Journal of Econometrics, 64: 183-206.
errors.
Journal of Econometrics, 64: 183-206.
- 14
-
Chib, S. and Greenberg, E. (1995).
Understanding the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm.
American Statistician, 49: 327-335.
- 15
-
Chib, S. and Greenberg, E. (1996).
Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation methods in econometrics.
Econometric Theory, 12: 409-431.
- 16
-
Chib, S. Greenberg, E. and Winklemann, R. (1998).
Posterior simulation and Bayes factors in panel count data models.
Journal of Econometrics, 86, 33-54.
- 17
-
Chib, S. and Jeliazkov, I. (2001).
Marginal likelihood from the Metropolis-Hastings output.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 96: 270-281.
- 18
-
Congdon, P. (20011).
Bayesian Statistical Modeling, John Wiley, Chicester.
- 19
-
Cowles, M.K. and Carlin, B. (1996).
Markov chain Monte Carlo convergence diagnostics: A comparative review.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 91: 883-904.
- 20
-
Damien, P., Wakefield, J. and Walker, S. (1999).
Gibbs Sampling for Bayesian nonconjugate and hierarchical models using auxiliary variables.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 61, 331-344.
- 21
-
Fahrmeir, L. and Tutz, G. (1997).
Multivariate Statistical Modeling Based on Generalized Linear Models.
Springer Verlag, New York.
- 22
-
Gammerman, D. (1997).
Markov chain Monte Carlo: Stochastic Simulation for Bayesian Inference.
Chapman and Hall, London.
- 23
-
Gelfand, A.E. and Smith, A.F.M. (1990).
Sampling-based approaches to calculating marginal densities.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 85: 398-409.
- 24
-
Gelman, A. and Rubin, D.B. (1992).
Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences.
Statistical Science, 4: 457-472.
- 25
-
Gelman, A., Meng, X.L., Stern, H.S. and Rubin, D.B.(2003).
Bayesian Data Analysis, (2nd ed), Chapman and Hall, London.
- 26
-
Geman, S. and Geman, D. (1984).
Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions and the Bayesian restoration of images.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 12: 609-628.
- 27
-
Geweke, J. (1989).
Bayesian inference in econometric models using Monte Carlo integration.
Econometrica, 57: 1317-1340.
- 28
-
Geweke, J. (1992).
Evaluating the accuracy of sampling-based approaches to the calculation of posterior moments.
In Bernardo, J.M., Berger, J.O., Dawid, A.P. and Smith, A.F.M. (eds),
Bayesian Statistics, pp. 169-193, Oxford University Press, New York.
- 29
-
Geyer, C. (1992).
Practical Markov chain Monte Carlo.
Statistical Science, 4: 473-482.
- 30
-
Geyer, C. and Thompson, E.A. (1995).
Annealing Markov chain Monte Carlo with Applications to Ancestral Inference.
Journal of American Statistical Association, 90: 909-920.
- 31
-
Gilks, W.R., Richardson, S. and Spiegelhalter, D.J. (1996).
Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice, Chapman and Hall, London.
- 32
-
Hastings, W. K. (1970).
Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications.
Biometrika 57: 97-109.
- 33
-
Liu, J.S. (1994).
The collapsed Gibbs sampler in Bayesian computations with applications to a gene
regulation problem.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89: 958-966.
- 34
-
Liu, J. S. (2001),
Monte Carlo Strategies in Scientific Computing, Springer Verlag, New York.
- 35
-
Liu, J.S., Wong, W.H. and Kong, A. (1994).
Covariance structure of the Gibbs Sampler with applications to
the comparisons of estimators and data augmentation schemes.
Biometrika, 81: 27-40.
- 36
-
Liu, J.S., Wong, W.H. and Kong, A. (1995).
Covariance structure and convergence rate of the Gibbs sampler with various scans.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 57: 157-169.
- 37
-
Marinari, E. and Parsi, G. (1992).
Simulated tempering: A new Monte Carlo scheme.
Europhysics Letters, 19: 451-458.
- 38
-
Mengersen, K.L. and Tweedie, R.L. (1996).
Rates of convergence of the Hastings and Metropolis algorithms.
Annals of Statistics, 24: 101-121.
- 39
-
Metropolis, N., Rosenbluth, A.W., Rosenbluth, M.N., Teller, A.H. and Teller, E. (1953).
Equations of state calculations by fast computing machines.
Journal of Chemical Physics, 21: 1087-1092.
- 40
-
Meyn, S.P. and Tweedie, R.L. (1993).
Markov chains and stochastic stability. Springer-Verlag, London.
- 41
-
Mira, A. and Tierney, L. (2002).
Efficiency and convergence properties of slice samplers.
Scandinavian Journal Of Statistics, 29: 1-12.
- 42
-
Nummelin, E. (1984).
General irreducible Markov chains and non-negative operators.
Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
- 43
-
Polson, N. G. (1996).
Convergence of Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithms.
In Bernardo, J.M., Berger, J.O., Dawid, A.P. and Smith, A.F.M. (eds),
Proceedings of the Fifth Valencia International Conference on Bayesian Statistics,
pp. 297-323, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- 44
-
Propp, J.G. and Wilson, D.B. (1996).
Exact sampling with coupled Markov chains and applications to statistical mechanics.
Random Structures and Algorithms, 9: 223-252.
- 45
-
Raftery, A. E. and Lewis, S.M. (1992).
How many iterations in the Gibbs sampler?
In Bernardo, J.M., Berger, J.O., Dawid, A.P. and Smith, A.F.M. (eds),
Proceedings of the Fourth Valencia International Conference on Bayesian Statistics,
pp. 763-774, Oxford University Press, New York.
- 46
-
Ripley, B. (1987).
Stochastic simulation, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
- 47
-
Ritter, C, and Tanner, M.A. (1992).
Facilitating the Gibbs Sampler: the Gibbs Stopper and the Griddy-Gibbs Sampler.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 87: 861-868.
- 48
-
Robert C.P. (1995).
Convergence control methods for Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms.
Statistical Science, 10: 231-253.
- 49
-
Robert, C.P. (2001).
Bayesian Choice, 2nd ed, Springer Verlag, New York.
- 50
-
Robert, C.P. and Casella, G. (1999).
Monte Carlo Statistical Methods, Springer Verlag, New York.
- 51
-
Roberts, G.O. and Rosenthal, J.S. (1999).
Convergence of slice sampler Markov chains.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 61: 643-660.
- 52
-
Roberts, G.O. and Sahu, S.K. (1997).
Updating schemes, correlation structure, blocking, and parametization for the Gibbs sampler.
Journal of the Royal Statististical Society B, 59: 291-317.
- 53
-
Roberts, G.O. and Smith, A.F.M. (1994).
Some simple conditions for the convergence of the Gibbs sampler and
Metropolis-Hastings algorithms.
Stochastic Processes and its Applications, 49: 207-216.
- 54
-
Roberts, G.O. and Tweedie, R.L. (1996).
Geometric convergence and central limit theorems for
multidimensional Hastings and Metropolis algorithms.
Biometrika, 83: 95-110.
- 55
-
Rosenthal, J.S. (1995).
Minorization conditions and convergence rates for Markov chain Monte Carlo.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90: 558-566.
- 56
-
Smith, A.F.M. and Roberts, G.O. (1993).
Bayesian computation via the Gibbs sampler and related Markov chain Monte Carlo methods.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 55: 3-24.
- 57
-
Tanner, M.A. (1996).
Tools for Statistical Inference, 3rd ed, Springer-Verlag, New York.
- 58
-
Tanner, M.A. and Wong, W.H. (1987).
The calculation of posterior distributions by data augmentation.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 82: 528-549.
- 59
-
Tierney, L. (1994).
Markov chains for exploring posterior distributions (with discussion).
Annals of Statistics, 22: 1701-1762.
- 60
-
Zellner, A. and Min, C. (1995).
Gibbs sampler convergence criteria.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90: 921-927.
Subsections