



Next: 10. Semiparametric Models
Up: csahtml
Previous: 9.5 Analysis of Variance
-
- 1
-
Adrover, J. (1998).
Minimax bias-robust estimation of the dispersion matrix of
multivariate distributions. Annals of Statistics, 26:2301-2320.
- 2
-
Andrews, D.F., Bickel, P.J., Hampel, F.R., Rogers, W.H., and Tukey, J.W.
(1972).
Robust Estimates of Location: Survey and Advances.
Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J.
- 3
-
Atkinson, A.C. (1994).
Fast very robust methods for the detection of multiple outliers.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89:1329-1339.
- 4
-
Barme-Delcroix, M.-F. and Gather, U. (2000).
An isobar-surfaces approach to multidimensional outlier-proneness.
Technical Report 20, Sonderforschungsbereich 475, University of
Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany.
- 5
-
Barnett, V. and Lewis, T. (1994).
Outliers in Statistical Data.
Wiley, New York, third edition.
- 6
-
Bartlett, M.S. (1935).
The effect of non-normality on the
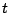 -distribution.
Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
31:223-231.
-distribution.
Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
31:223-231.
- 7
-
Becker, C. and Gather, U. (1999).
The masking breakdown point of multivariate outlier identification
rules.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 94:947-955.
- 8
-
Becker, C. and Gather, U. (2001).
The largest nonidentifiable outlier: a comparison of multivariate
simultaneous outlier identification rules.
Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 36:119-127.
- 9
-
Bednarski, T. (1993).
Fréchet differentiability and robust estimation.
In Mandl, P. and Husková, M. (eds), Asymptotic Statistics:
Proceedings of the Fifth Prague Symposium, Springer Lecture Notes,
pp.49-58. Springer.
- 10
-
Bednarski, T. and Clarke, B.R. (1998).
On locally uniform expansions of regular functionals.
Discussiones Mathematicae: Algebra and Stochastic Methods,
18:155-165.
- 11
-
Bednarski, T., Clarke, B.R., and Kolkiewicz, W. (1991).
Statistical expansions and locally uniform Fréchet
differentiability.
Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society, 50:88-97.
- 12
-
Bernholt, T. and Fischer, P. (2001).
The complexity of computing the mcd-estimator.
Technical Report 45, Sonderforschungsbereich 475, University of
Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany.
- 13
-
Berrendero, J.R. and Zamar, R.H. (2001).
Maximum bias curves for robust regression with non-elliptical
regressors.
Annals of Statistics, 29:224-251.
- 14
-
Box, G.E.P. (1953).
Non-normality and test on variance.
Biometrika, 40:318-335.
- 15
-
Box, G.E.P. and Andersen, S.L. (1955).
Permutation theory in the derivation of robust criteria and the study
of departures from assumption.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 17:1-34.
- 16
-
Caroni, C. and Prescott, P. (1992).
Sequential application of wilk's multivariate outlier test.
Applied Statistics, 41:355-364.
- 17
-
Chang, H., McKean, J.W., Narjano, J.D., and Sheather, S.J. (1999).
High-breakdown rank regression.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
94(445):205-219.
- 18
-
Clarke, B.R. (1983).
Uniqueness and Fréchet differentiability of functional
solutions to maximum likelihood type equations.
Annals of Statistics, 11:1196-1205.
- 19
-
Cohen, M. (1991).
The background of configural polysampling: a historical perspective.
In Morgenthaler, S. and Tukey, J.W. (eds), Configural
Polysampling: A Route to Practical Robustness, Chap. 2. Wiley, New York.
- 20
-
Croux, C. and Dehon, C. (2001).
Robust linear discriminant analysis using S-estimators.
Canadian Journal of Statistics, 29:473-492.
- 21
-
Croux, C. and Haesbroeck, G. (2000).
Principal components analysis based on robust estimators of the
covariance or correlation matrix: influence functions and efficiencies.
Biometrika, 87:603-618.
- 22
-
Croux, C. and Rousseeuw, P.J. (1992).
Time-efficient algorithms for two highly robust estimators of scale.
In Dodge, Y. and Whittaker, J.C. (eds), Computational
Statistics, volume 1, pp.411-428, Heidelberg. Physica-Verlag.
- 23
-
Davies, P.L. (1987).
Asymptotic behaviour of S-estimates of multivariate location
parameters and dispersion matrices.
Annals of Statistics, 15:1269-1292.
- 24
-
Davies, P.L. (1992a).
The asymptotics of Rousseeuw's minimum volume ellipsoid.
Annals of Statistics, 20:1828-1843.
- 25
-
Davies, P.L. (1993).
Aspects of robust linear regression.
Annals of Statistics, 21:1843-1899.
- 26
-
Davies, P.L. (1995).
Data features.
Statistica Neerlandica, 49:185-245.
- 27
-
Davies, P.L. (1998).
On locally uniformly linearizable high breakdown location and scale
functionals.
Annals of Statistics, 26:1103-1125.
- 28
-
Davies, P.L. (2004).
The one-way table.
Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 122:3-13.
- 29
-
Davies, P.L. and Gather, U. (1993).
The identification of multiple outliers (with discussion).
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88:782-801.
- 30
-
Dietel, G. (1993).
Global location and dispersion functionals.
PhD thesis, University of Essen.
- 31
-
Donoho, D.L. (1982).
Breakdown properties of multivariate location estimators.
PhD thesis, Department of Statistics, Harvard University, Harvard,
Mass.
- 32
-
Donoho, D.L. and Gasko, M. (1992).
Breakdown properties of location estimates based on halfspace depth
and project outlyingness.
Annals of Statistics, 20:1803-1827.
- 33
-
Donoho, D.L. and Huber, P.J. (1983).
The notion of breakdown point.
In Bickel, P.J., Doksum, K.A. and Hodges, J.L. Jr. (eds), A Festschrift for Erich L. Lehmann, pp. 157-184, Belmont, California.
Wadsworth.
- 34
-
Eddington, A.S. (1914).
Stellar Movements and the Structure of the Universe.
Macmillan, New York.
- 35
-
Edelsbrunner, H. and Souvaine, D. (1990).
Computing median-of-squares regression lines and guided topological
sweep.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 85:115-119.
- 36
-
Ellis, S.P. (1998).
Instability of least squares, least absolute deviation and least
median of squares linear regression.
Statistical Science, 13(4):337-350.
- 37
-
Fernholz, L.T. (1983).
Von Mises Calculus for Statistical Functionals.
Number 19 in Lecture Notes in Statistics. Springer-Verlag, New York.
- 38
-
Fisher, R.A. (1920).
A mathematical examination of the methods of determining the accuracy
of an observation by the mean error and the mean square error.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 80:758-770.
- 39
-
Fisher, R.A. (1935).
The Design of Experiments,
Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh and London.
- 40
-
Gather, U. (1990).
Modelling the occurrence of multiple outliers.
Allgemeines Statistisches Archiv, 74:413-428.
- 41
-
Gather, U. and Hilker, T. (1997).
A note on tyler's modification of the MAD for the stahel-donoho
estimator.
Annals of Statistics, 25:2024-2026.
- 42
-
Gather, U., Kuhnt, S., and Pawlitschko, J. (2003).
Concepts of outlyingness for various data structures.
In Misra, J.C. (ed), Industrial Mathematics and Statistics.
Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, 545-585.
- 43
-
Gather, U. and Schultze, V. (1999).
Robust estimation of scale of an exponential distribution.
Statistica Neerlandica, 53:327-341.
- 44
-
Gayen, A.K. (1950).
The distribution of the variance ratio in random samples of any size
drawn from non-normal universe.
Biometrika, 37:236-255.
- 45
-
Geary, R.C. (1936).
The distribution of 'student's' ratio for non-normal samples.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Supplement,
3:178-184.
- 46
-
Geary, R.C. (1947).
Testing for normality.
Biometrika, 34:209-242.
- 47
-
Gervini, D. and Yohai, V.J. (2002).
A class of robust and fully efficient regression estimators.
Annals of Statistics, 30(2):583-616.
- 48
-
Gnanadesikan, R. and Kettenring, J.R. (1972).
Robust estimates, residuals, and outlier detection with multiresponse
data.
Biometrics, 28:81-124.
- 49
-
Hadi, A.S. (1994).
A modification of a method for the detection of outliers in
multivariate samples.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B,
56:393-396.
- 50
-
Hadi, A.S. and Simonoff, J.S. (1997).
Procedures for the identification of multiple outliers in linear
models.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88:1264-1272.
- 51
-
Hampel, F.R. (1968).
Contributions to the theory of robust estimation.
PhD thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
- 52
-
Hampel, F.R. (1975).
Beyond location parameters: Robust concepts and methods (with
discussion).
In Proceedings of the 40th Session of the ISI, volume 46, Book 1, pp.375-391.
- 53
-
Hampel, F.R. (1985).
The breakdown points of the mean combined with some rejection rules.
Technometrics, 27:95-107.
- 54
-
Hampel, F.R., Ronchetti, E.M., Rousseeuw, P.J., and Stahel, W.A. (1986).
Robust Statistics: The Approach Based on Influence Functions,
Wiley, New York.
- 55
-
Hawkins, D.M. (1980).
Identification of outliers,
Chapman and Hall, London.
- 56
-
Huber, P.J. (1964).
Robust estimation of a location parameter.
Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 35:73-101.
- 57
-
Huber, P.J. (1977).
Robust statistical procedures.
In Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics No. 27,
Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, Penn.
- 58
-
Huber, P.J. (1981).
Robust Statistics,
Wiley, New York.
- 59
-
Huber, P.J. (1984).
Finite sample breakdown points of m- and p-estimators.
Annals of Statistics, 12:119-126.
- 60
-
Huber, P.J. (1995).
Robustness: Where are we now?
Student, 1:75-86.
- 61
-
Kent, J.T. and Tyler, D.E. (1991).
Redescending M-estimates of multivariate location and scatter.
Annals of Statistics, 19:2102-2119.
- 62
-
Kent, J.T. and Tyler, D.E. (1996).
Constrained M-estimation for multivariate location and scatter.
Annals of Statistics, 24:1346-1370.
- 63
-
Liu, R.Y., Parelius, J.M., and Singh, K. (1999).
Multivariate analysis by data depth: descriptive statistics, graphics
and inference.
Annals of Statistics, 27:783-840.
- 64
-
Lopuhaä, H.P. (1989).
On the relation between S-estimators and M-estimators of
multivariate location and covariance.
Annals of Statistics, 19:229-248.
- 65
-
Lopuhaä, H.P. (1991).
Multivariate
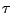 -estimators for location and scatter.
Canadian Journal of Statistics, 19:307-321.
-estimators for location and scatter.
Canadian Journal of Statistics, 19:307-321.
- 66
-
Lopuhaä, H.P. and Rousseeuw, P.J. (1991).
Breakdown properties of affine equivariant estimators of multivariate
location and covariance matrices.
Annals of Statistics, 19:229-248.
- 67
-
Marazzi, A. (1992).
Algorithms, Routines, and S- Functions for Robust Statistics.
Chapman and Hall, New York.
- 68
-
Maronna, R.A. (1976).
Robust M-estimators of multivariate location and scatter.
Annals of Statistics, 4(1):51-67.
- 69
-
Maronna, R.A., Stahel, W.A., and Yohai, V.J. (1992).
Bias-robust estimators of multivariate scatter based on projections.
Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 42:141-161.
- 70
-
Maronna, R.A. and Yohai, V.J. (1981).
Asymptotic behavior of general M-estimates for regression and scale
with random carriers.
Zeitschrift für Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie und verwandte
Gebiete, 58:7-20.
- 71
-
Maronna, R.A. and Yohai, V.J. (1993).
Bias-robust estimates of regression based on projections.
Annals of Statistics, 21(2):965-990.
- 72
-
Martin, R.D., Yohai, V.J., and Zamar, R.H. (1989).
Min-max bias robust regression.
Annals of Statistics, 17(4):1608-1630.
- 73
-
Martin, R.D. and Zamar, R.H. (1993a).
Bias robust estimation of scale.
Annals of Statistics, 21(2):991-1017.
- 74
-
Martin, R.D. and Zamar, R.H. (1993b).
Efficiency constrained bias robust estimation of location.
Annals of Statistics, 21(1):338-354.
- 75
-
Mendes, B. and Tyler, D.E. (1996).
Constrained M-estimates for regression.
In Rieder, H. (ed), Robust Statistics; Data Analysis and
Computer Intensive Methods, number 109 in Lecture Notes in Statistics,
pp.299-320. Springer-Verlag.
- 76
-
Neyman, J. and Pearson, E.S. (1933).
On the problem of the most efficient tests of statistical hypotheses.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society (London), Series
A, 231:289-337.
- 77
-
Pearson, E.S. (1929).
The distribution of frequency constants in small samples from
non-normal symmetrical and skew populations.
Biometrika, 21:259-286.
- 78
-
Pearson, E.S. (1931).
The analysis of variance in cases of non-normal variation.
Biometrika, 23:114-133.
- 79
-
Pearson, E.S. and Chandra Sekar, S. (1936).
The efficiency of statistical tools and a criterion for the rejection
of outlying observations.
Biometrika, 28:308-320.
- 80
-
Pollard, D. (1984).
Convergence of stochastic processes.
Springer-Verlag, New York.
- 81
-
Riedel, M. (1989a).
On the bias-robustness in the location model i.
Statistics, 2:223-233.
- 82
-
Riedel, M. (1989b).
On the bias-robustness in the location model ii.
Statistics, 2:235-246.
- 83
-
Rieder, H. (1994).
Robust Asymptotic Statistics.
Springer, Berlin.
- 84
-
Rocke, D.M. (1996).
Robustness properties of S-estimators of multivariate location and
shape in high dimension.
Annals of Statistics, 24:1327-1345.
- 85
-
Rocke, D.M. and Woodruff, D.L. (1996).
Identification of outliers in multivariate data.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
91(435):1047-1061.
- 86
-
Rocke, D.M. and Woodruff, D.L. (1997).
Robust estimation of multivariate location and shape.
Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 91:245-255.
- 87
-
Rosner, B. (1975).
On the detection of many outliers.
Technometrics, 17:221-227.
- 88
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. (1984).
Least median of squares regression.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 79:871-880.
- 89
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. (1985).
Multivariate estimation with high breakdown point.
In Grossmann, W., Pflug, C.G., Vincze, I. and Wertz, W. (eds),
Mathematical Statistics and Applications (Proceedings of the 4th
Pannonian Symposium on Mathematical Statistics), volume B, Dordrecht.
Reidel.
- 90
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Croux, C. (1992).
Explicit scale estimators with high breakdown point.
In Dodge, Y. (ed),
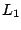 -Statistical Analysis and Related
Methods, pp.77-92, Amsterdam. North Holland.
-Statistical Analysis and Related
Methods, pp.77-92, Amsterdam. North Holland.
- 91
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Croux, C. (1993).
Alternatives to the median absolute deviation.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88:1273-1283.
- 92
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Croux, C. (1994).
The bias of k-step M-estimators.
Statistics and Probability Letters, 20:411-420.
- 93
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Hubert, M. (1999).
Regression depth.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 94:388-402.
- 94
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Leroy, A.M. (1987).
Robust Regression and Outlier Detection,
Wiley, New York.
- 95
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Van Driesen, K. (1999).
A fast algorithm for the minimum covariance determinant estimator.
Technometrics, 41:212-223.
- 96
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Van Driesen, K. (2000).
An algorithm for positive-breakdown methods based on concentration
steps.
In Gaul, W., Opitz, O., and Schader, M. (eds), Data Analysis:
Scientific modelling and Practical Application, pp.335-346.
Springer-Verlag, New York.
- 97
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and van Zoomeren, B.C. (1990).
Unmasking multivariate outliers and leverage points.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 85:633-639.
- 98
-
Rousseeuw, P.J. and Yohai, V.J. (1984).
Robust regression by means of S-estimators.
In Franke, J. e.a. (ed), Robust and Nonlinear Time Series
Analysis, pp.256-272, New York. Springer.
- 99
-
Scholz, F.W. (1971).
Comparison of optimal location estimators.
PhD thesis, Department of Statistics, University of California,
Berkley.
- 100
-
Sheather, S.J., McKean, J.W., and Hettmansperger, T.P. (1997).
Finite sample stability properties of the least median of squares
estimator.
Journal of Statistical Computing and Simulation,
58(4):371-383.
- 101
-
Simonoff, J.S. (1984).
A comparison of robust methods and detection of outlier techniques
when estimating a location parameter.
Communications in Statistics, Series A, 13:813-842.
- 102
-
Simonoff, J.S. (1987).
The breakdown and influence properties of outlier rejection-plus-mean
procedures.
Communications in Statistics, Series A, 16:1749-1760.
- 103
-
Stahel, W.A. (1981).
Breakdown of covariance estimators.
Research Report 31, Fachgruppe für Statistik, ETH, Zurich.
- 104
-
Staudte, R.G. and Sheather, S.J. (1990).
Robust Estimation and Testing,
Wiley, New York.
- 105
-
Tatsuoka, K.S. and Tyler, D.E. (2000).
On the uniqueness of S-functionals and M-functionals under
non-elliptic distributions.
Annals of Statistics, 28(4):1219-1243.
- 106
-
Terbeck, W. and Davies, P.L. (1998).
Interactions and outliers in the two-way analysis of variance.
Annals of Statistics, 26:1279-1305.
- 107
-
Tietjen, G.L. and Moore, R.H. (1972).
Some grubbs-type statistics for the detection of several outliers.
Technometrics, 14:583-597.
- 108
-
Tukey, J.W. (1960).
A survey of sampling from contaminated distributions.
In Olkin, I. (ed), Contributions to Probability and
Statistics. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
- 109
-
Tukey, J.W. (1975).
Mathematics and picturing data.
In Proceedings of International Congress of Mathematicians,
Vancouver, volume 2, pp.523-531.
- 110
-
Tukey, J.W. (1993).
Exploratory analysis of variance as providing examples of strategic
choices.
In Morgenthaler, S., Ronchetti, E., and Stahel, W.A. (eds), New Directions in Statistical Data Analysis and Robustness, Basel.
Birkhäuser.
- 111
-
Tyler, D.E. (1994).
Finite sample breakdown points of projection based multivariate
location and scatter statistics.
Annals of Statistics, 22:1024-1044.
- 112
-
von Mises, R. (1937).
Sur les fonctions statistiques.
In Conférence de la Réunion Internationale des
Mathématiciens. Gauthier-Villars.
- 113
-
Willems, S., Pison, G., Rousseeuw, P.J., and Van Aelst, S. (2002).
A robust Hotelling test.
Metrika, 55:125-138.
- 114
-
Yohai, V.J. (1987).
High breakdown point and high efficiency robust estimates for
regression.
Annals of Statistics, 15:642-656.
- 115
-
Yohai, V.J. and Maronna, R.A. (1990).
The maximum bias of robust covariances.
Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods,
19:3925-3933.
- 116
-
Yohai, V.J. and Zamar, R.H. (1988).
High breakdown point estimates of regression by means of the
minimization of an efficient scale.
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83:406-413.
- 117
-
Zuo, Y. (2001).
Some quantitative relationships between two types of finite sample
breakdown points.
Statistics and Probability letters, 51:369-375.
- 118
-
Zuo, Y. and Serfling, R. (2000a).
General notions of statistical depth function.
Annals of Statistics, 28:461-482.
- 119
-
Zuo, Y. and Serfling, R. (2000b).
Structural properties and convergence results for contours of sample
statistical depth functions.
Annals of Statistics, 28:483-499.
Subsections